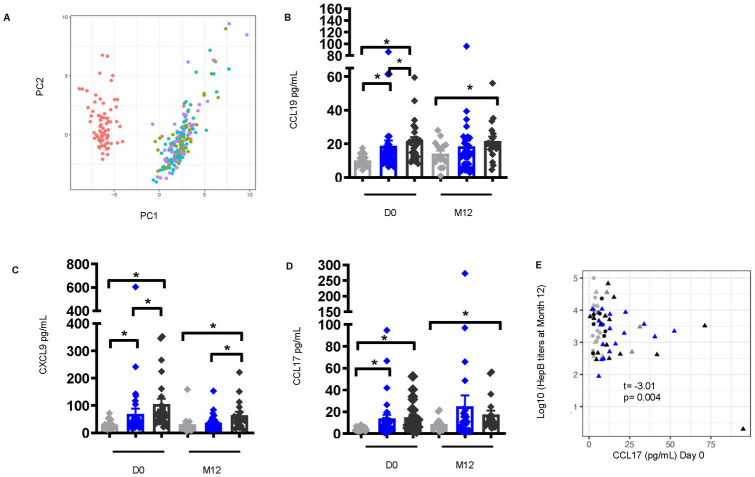
Fig 3. Elevated levels of plasma cytokines/chemokines involved in lymphocyte cell migration and activation pre-vaccination in individuals with S. mansoni infection persist at month 12 post-vaccination.
(A) Principal component analysis of plasma cytokines/chemokines pre-vaccination and after Hepatitis B vaccination was conducted and the first (PC1) and second (PC2) principal components were used to plot samples based on their plasma cytokines/chemokines profiles. Each dot corresponds to a sample and colors denote the timepoint the sample was collected. [D0- red, D3- green, D7- blue, and M12- purple]. Plasma levels of (B) CCL19, (C) CXCL9, and (D) CCL17 [non-infected pre-vaccination (D0), n = 19, low CAA, n = 32, and high CAA, n = 24; M12 post-vaccination, n = 15, low CAA, n = 29, and high CAA, n = 19]. Data shown as ± SEM. * P ≤ 0.05. Wilcoxon rank-sum test performed on non-infected vs. low CAA, or non-infected vs. high CAA, or low CAA vs. high CAA within each time point D0 or M12. Non-infected- light grey, low CAA—blue, and high CAA—dark grey. (E) Scatter plot of Hepatitis B titers at M12 as a function of plasma CCL17 cytokine levels at D0 [non-infected, n = 19, low CAA, n = 32, high CAA, n = 24]. Linear regressions were fit between Hepatitis B titers and the cytokines adjusted for sex and student t-tests were used to evaluate for the significance of the association. t (t-statistic). P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. (Shape: circle-females, triangle-males; color: grey- non-infected, black-low CAA, blue- high CAA).