Figure 2.
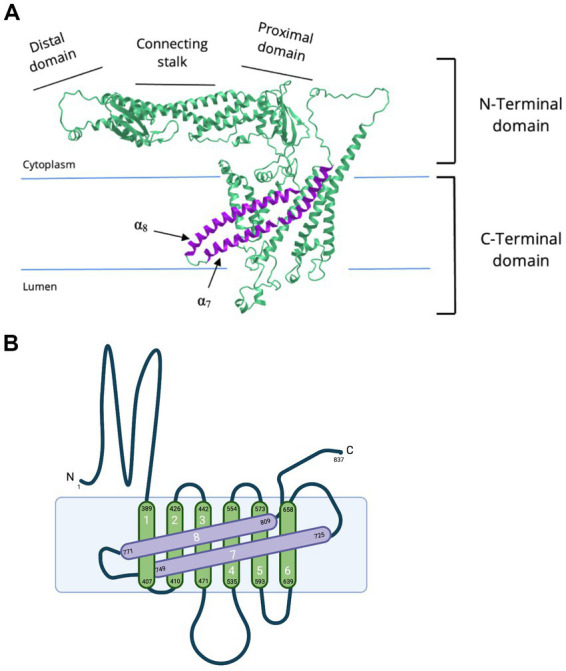
Cryo-EM of NTD and CTD of subunit a1. (A) Cryo-EM derived structure of the human V-ATPase subunit a (RCSB PDB: 6WLW, source: iCN3D) (Wang J. et al., 2020; Wang L. et al., 2020) and (B) a simplified topology representation of V-ATPase subunit a1. Subunit a1 is made up of two domains, a cytoplasmic NTD and membrane-embedded CTD. The a1-NTD is composed of a distal domain, connecting stalk, and proximal domain. a1-CTD consists of eight transmembrane α-helices connected by short linker loops on both cytoplasmic and luminal sides. a1-CTD is important for proton translocation. Transmembrane helices α7-α8 (in purple) are tilted. These transmembrane helices compose part of the hemichannels and hold important residues for proton translocation (R740 at α7 and R804 at α8). (B) was created with BioRender.com.
