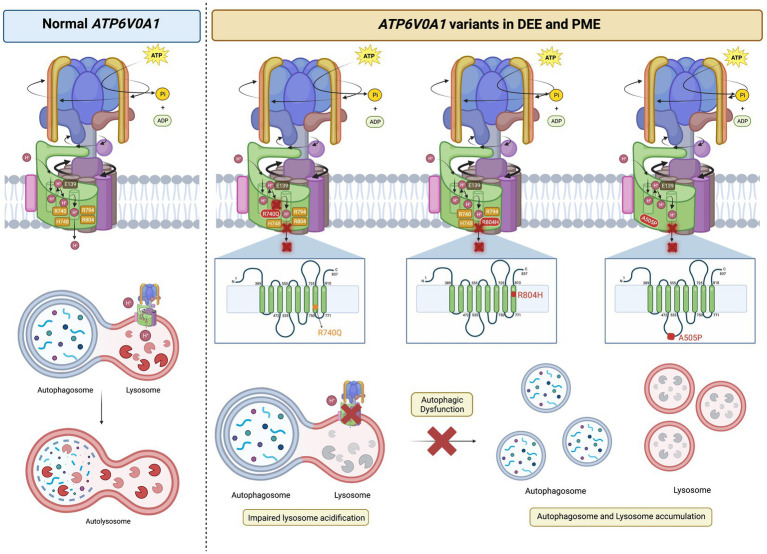
Figure 4.
ATP6V0A1 variants implicated in DEE and PME cause lysosomal and autophagic dysfunction. Normal ATP6V0A1 encodes for a functional subunit a1 of the V-ATPase, which couples ATP hydrolysis and proton translocation through the c-ring. Protons are pumped into the lumen of lysosomes to achieve a pH of ~5.5 for optimal enzymatic activities in autophagosome clearance. On the other hand, variants of ATP6V0A1 compromise V-ATPase function and interfere with proper lysosomal acidification, leading to the accumulation of autophagosome and lysosomal bodies, as reported in cases of DEE and PME. R740Q mutant was reported in DEE and PME patients, while R804 and A505P were found in DEE patients (Aoto et al., 2021; Bott et al., 2021). Based on studies in animal models by Aoto et al. (2021) and Bott et al. (2021), R740Q and R804H in the 7th and 8th transmembrane region, respectively, are key residues in the proton translocation, adversely affected by such substitutions. A505P variant on the 2nd luminal linker region is also implicated in DEE, affecting autophagic function (Aoto et al., 2021). It is still unclear how A505P impairs V-ATPase function in autophagic dysfunction. The figure was created with BioRender.com.