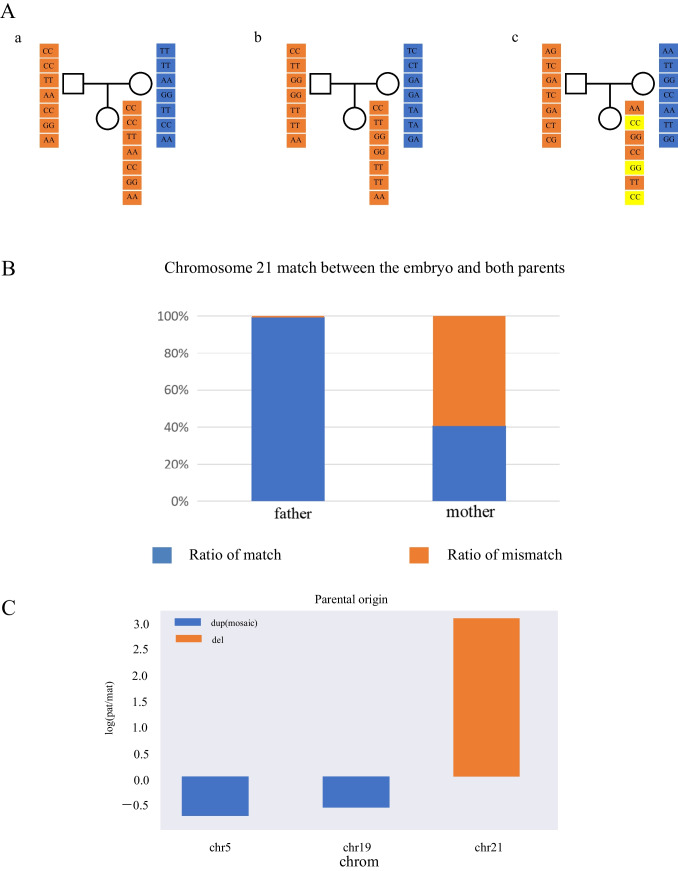
Fig. 4.
Verification of the parental origin of the copy number variation fragments. A-a Assuming that parents are homozygous, embryo genotype matching model. When both parents are homozygous, if the male genotype is AA and the female genotype is BB, the normal embryo will inherit the male allele A and the female allele B theoretically. Because the embryo chromosome is monosomy 21, if the embryo has genotype AA at this locus, it will be counted as the matched paternal chromosome; otherwise, it will be counted as the matched maternal chromosome. b Assuming that the male is homozygous and the female is heterozygous, embryo genotype matching model. When the male genotype is AA and the female genotype is AB, the normal embryo must inherit the male genotype A theoretically. Since the embryo chromosome is monosomy 21, if the genotype of this site in the embryo is AA, it will be considered as matching the paternal source. c Assuming that the male is heterozygous and the female is homozygous, embryo genotype matching model. When the male genotype is AB and the female genotype is AA, if the embryo genotype is AA, it is considered to match the maternal source. Orange square denotes maternal genotype. Blue square denotes paternal genotype. Yellow square denotes embryo genotype did not matching either parent. B The matching ratio was calculated according to the above method. Blue square denotes the matching ratio for the remaining chromosome 21 of the embryo for parents. Orange square denotes the mismatching ratio for the remaining chromosome 21 of the embryo for parents. C Above the 0 scale line, the chromosomal fragment is paternal, and below it, maternal. If the parental genotype is AA and BB, and the embryo is AA, so the maternal allele is 2 and the paternal allele is 0. Then, the parental ratio of the whole chromosome of the embryo was calculated. The parental ratio = the number of paternal alleles/the number of maternal alleles (for convenience of calculation, the parental ratio was taken as log). Finally, the parental chromosome composition of the embryo was inferred according to the parental ratio combined with the chromosome copy number. Theoretically, each pair of chromosomes of a normal individual was derived from the parents, and the parental ratio was 0. If the chromosome duplication exists, when the parental ratio is greater than 0, it means that there are superfluous paternal alleles in the embryo chromosome, and it is inferred that one chromosome duplication in the embryo is inherited from the father; otherwise, it is inherited from the mother. If a chromosome deletion is present, one of the remaining chromosomes in the embryo is presumed to have been inherited from the father when the parental ratio is greater than 0