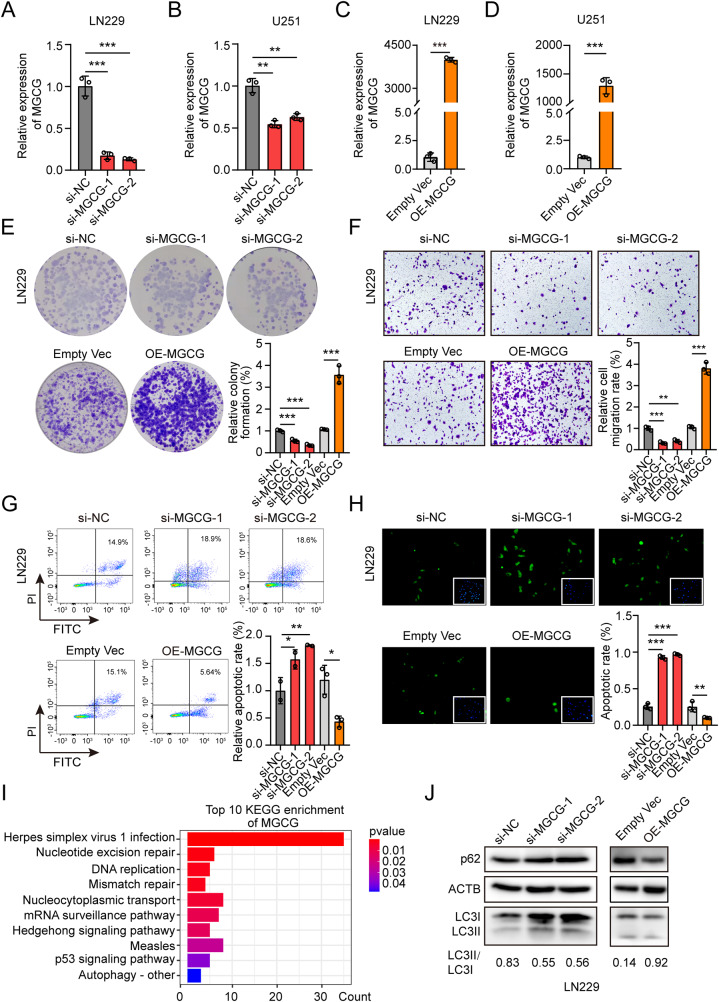
Fig. 2. MGCG promotes malignant properties of GBM progression and induces autophagy.
A The data of RT‒qPCR on the expression of MGCG in LN229 cells treated with si-NC and three independent siRNAs (si-MGCG1, si-MGCG2, and si-MGCG3). B The data of RT‒qPCR on the expression of MGCG in U251 cells treated with si-NC and three independent siRNAs (si-MGCG1, si-MGCG2, and si-MGCG3). C The data of RT‒qPCR on the expression of MGCG in LN229 cells treated with EMPTY VEC and OE-MGCG. D The data of RT‒qPCR on the expression of MGCG in U251 cells treated with EMPTY VEC and OE-MGCG. E Colony formation assays were used to detect the effect of MGCG knockdown or overexpression on the growth of LN229 cells. F Transwell assay shows the effects of MGCG knockdown or overexpression on the migration of LN229 cells. G The data of flow cytometry analysis revealed the effect of MGCG knockdown or overexpression on apoptosis of LN229 cells. H The data of TUNEL analysis demonstrate the effect of MGCG knockdown or overexpression on apoptosis of LN229 cells. I Top 10 KEGG pathway enrichment of MGCG. J Western blot analysis of the protein levels of p62 and LC3 after knockdown or overexpression of MGCG in LN229 cells. Error bars, SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s test.