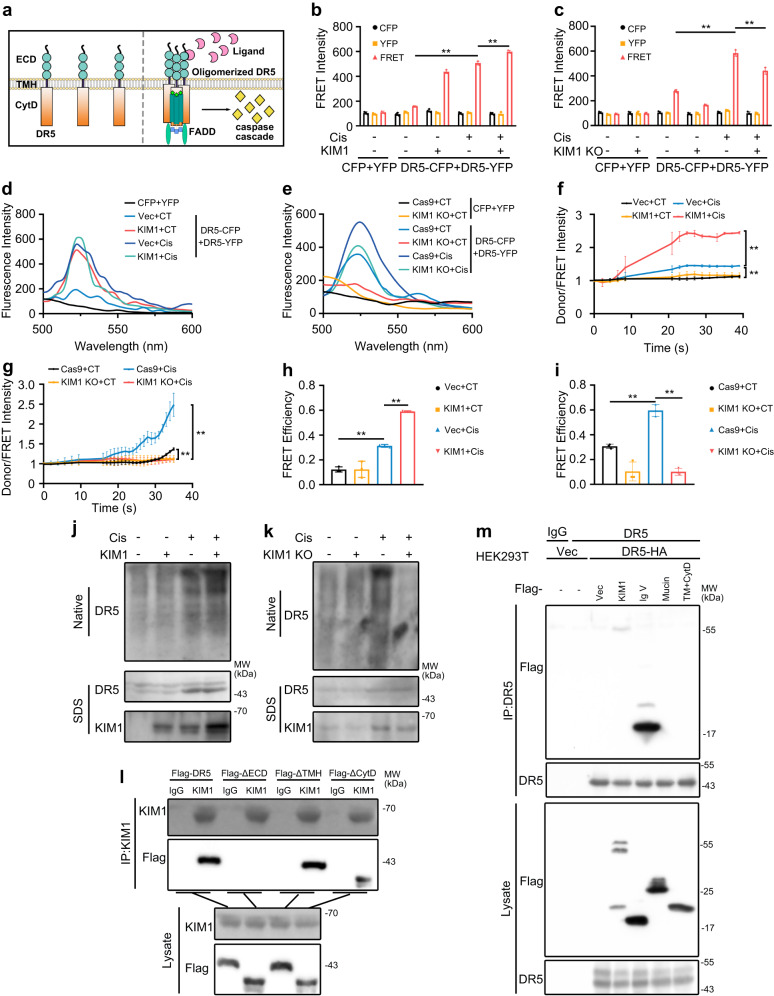
Fig. 5. KIM1 promotes the multimerization of DR5.
a Structural scheme of DR5 multimerization and downstream signaling pathways. Under physiological conditions, DR5 exists as a monomer, upon injury, ECD binds ligand and multimerizes, subsequently recruiting FADD with its CytD and activating the downstream caspase cascade. ECD ectodomain, CytD cytoplasmic domain. b–e Quantitative FRET indicating the effect of KIM overexpression (b) or knockdown (c) on DR5 multimerization following cisplatin injury, using fluorescence (d) or wavelength (e) scan. CFP, pRK-5′Flag-CFP; YFP, pRK-5′Flag-YFP; DR5-CFP, pRK-5′Flag-DR5-CFP; DR5-YFP, pRK-5′Flag-DR5-YFP; Vec, pRK-5′Flag; KIM1, pRK-5′Flag-KIM1; Cas9, lenti-CRISPR/Cas9; KIM1 KO, lenti-CRISPR/Cas9-based KIM1 knockout. b, c n = 3 biological samples per group, each experiment was repeated at least three times independently with similar results obtained; d, e Each experiment was repeated at least three times independently with similar results obtained. f, g Fluorescence redistribution after photobleaching (FRAP) assays showed the effect of KIM1 overexpression (f) or knockdown (g) on DR5 multimerization. f, g n = 3 biological samples per group, each experiment was repeated at least three times independently with similar results obtained. h, i FRET efficiency in KIM1 overexpression (h) or knockdown (i) groups. h, i n = 3 biological samples per group, each experiment was repeated at least three times independently with similar results obtained. j, k The effect of KIM1 overexpression (j) or knockdown (k) on the formation of higher-order DR5 oligomers detected using native PAGE electrophoresis. Each experiment was repeated at least three times independently with similar results obtained. l KIM1 bound to the ECD domain of DR5. A Co-IP assay was performed using anti-KIM1 or non-specific IgG as the negative control. For IP and lysate groups, KIM1 was detected with anti-KIM1 antibody; WT and mutants of DR5-Flag were detected using an anti-Flag antibody. m DR5 bound to the Ig V domain of KIM1. Co-IP assay was performed using anti-KIM1 or respective IgG, while IgG served as the negative control. For IP and lysate groups, Flag-tagged KIM1 truncations were detected with an anti-Flag antibody, and DR5-HA was detected using an anti-DR5 antibody. l, m Each experiment was repeated at least three times independently with similar results obtained. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test was used for two experimental groups, and one-way ANOVA for multiple experimental groups without adjustment. **P < 0.01. Exact P values are provided in Source Data.