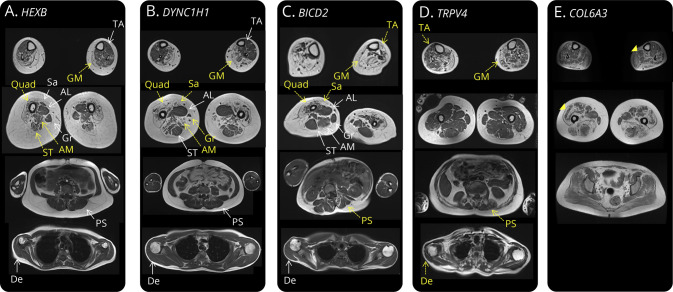
Figure 2. Differing MRI Muscle Involvement in Non-5q Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) Patients.
T1-weighted MRI sequences of 5 patients with variants in the 3 most frequent non-5q SMA genes (DYNC1H1, BICD2, and TRPV4) as well as in Sandhoff disease (HEXB) and COL6A3. Muscles with yellow arrows had marked fat replacement; muscles with white arrows were completely or partially spared. (A) Quadriceps, semitendinosus, and adductor magnus muscle degeneration in a patient with Sandhoff disease presenting as P-SMA. (B) The previously described quadriceps muscle degeneration with adductor longus and semitendinosus sparing in a patient with DYNC1H1 PD-SMA.19 In this case, sartorius and gracillis muscle fat replacement is also observed. (C) Quadriceps and sartorious muscle degeneration with more important lower limb involvement in a patient with BICD2 PD-SMA. Notice some degree of paraspinal muscle atrophy and important scoliosis. (D) Tibialis anterior and gastrocnemius medialis involvement with sparing of muscles of the thigh and paraspinal and deltoid muscle degeneration in a patient with TRPV4 SP-SMA. (E) Finally, the characteristic muscle fat replacement in a “sandwich patter” of soleus and quadriceps muscles (yellow arrowheads) in a patient with COL6A3 mutations and a pure SMA phenotype. AL = adductor longus; AM = adductor magnus; De = deltoid; GM = gastrocnemius medialis; Gr = gracillis; PS = paraspinal; Quad = quadriceps; Sa = sartorious; ST = semitendinosus; TA = tibialis anterior.