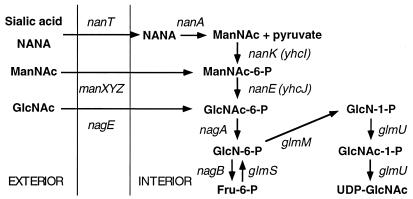
FIG. 1.
Pathway for the metabolism of GlcNAc and proposed pathway for the degradation of ManNAc and NANA (sialic acid). GlcNAc is transported by both the manXYZ-encoded transporter and its own specific transporter, encoded by nagE, producing intracellular GlcNAc-6-P, which is degraded by the nagA- and nagB-encoded enzymes. The biosynthetic pathway producing UDP-GlcNAc for incorporation into cell wall components involves the glmS, glmM, and glmU gene products. ManNAc is taken up by the manXYZ transporter, producing intracellular ManNAc-6-P. NANA is taken up as the free sugar by a sugar-cation symporter encoded by nanT. Inside the cell, NANA is cleaved by the aldolase encoded by nanA to give ManNAc and pyruvate. The results of this study allow us to propose that intracellular ManNAc is phosphorylated to ManNAc-6-P, which is subsequently converted to GlcNAc-6-P, the substrate of the nagA-encoded deacetylase. Thus, the pathways for degradation of NANA, ManNAc, and GlcNAc converge at the level of GlcNAc-6-P.