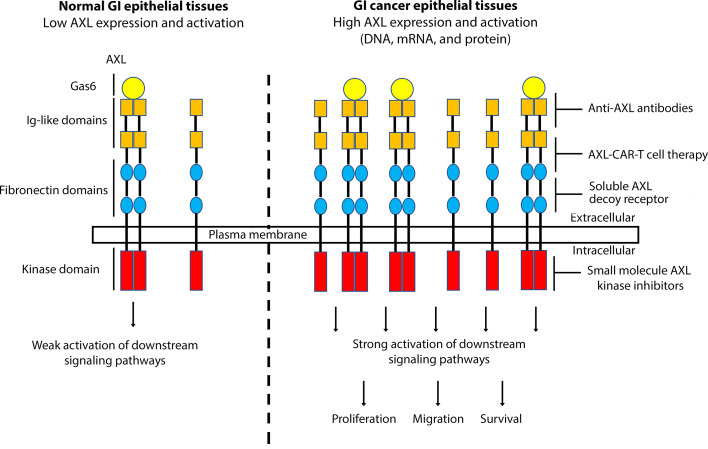
Figure 1.
A schematic representation depicting the role of AXL overexpression and activation in GI cancers. Overexpression of AXL, induced by DNA amplification or high mRNA and protein levels, in GI epithelial tissues leads to strong activation of downstream signaling pathways, promoting cell proliferation, migration, and survival, hallmarks of GI carcinogenesis. Targeting AXL with specific monoclonal antibodies, small molecule kinase inhibitors, soluble AXL decoy receptor, or CAR-T cell therapy could be effective as a targeted therapeutic approach in GI cancers.