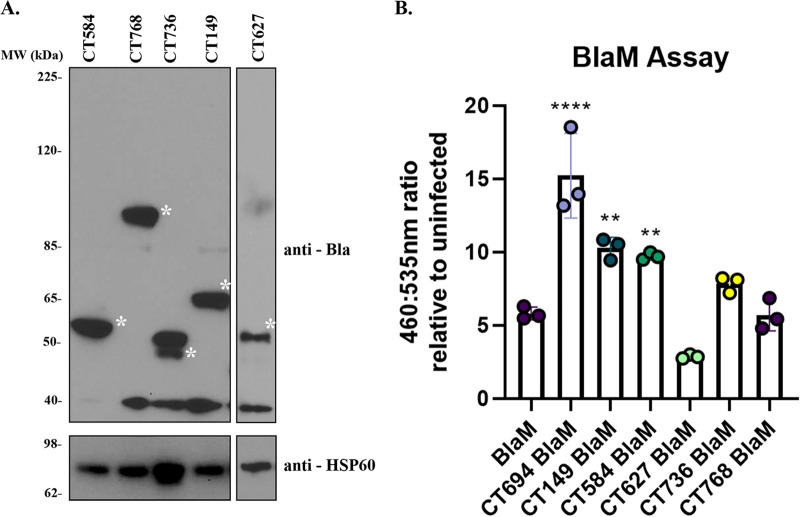
FIG 3.
Identification of novel secreted proteins from C. trachomatis via a beta-lactamase (BlaM) secretion assay. Candidate secretion substrates were fused to the BlaM tag and transformed into C. trachomatis. (A) HeLa cells were infected at an MOI of 5 for 24 h with transformants. Expression of the BlaM fusion protein was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-BlaM antibodies, and anti-HSP was used as a loading control. The asterisk indicates the molecular weight of each BlaM fusion protein. Predicted molecular weights are as follows: CT584-BlaM, 54 kDa; CT768-BlaM, 94 kDa; CT736-BlaM, 46 kDa; CT149-BlaM, 64 kDa; CT627, 68 kDa. (B) Secretion was determined by infecting HeLa cells at an MOI of 5 for 24 h. Infected cells were loaded with CCF4-AM for 1 h, and the change in 460-/535-nm fluorescence was monitored on a plate reader. A shift from 535-nm fluorescence to increased 460-nm fluorescence is indicative of secretion into the host cell cytosol. Ratios associated with the candidate substrate-BlaM fusions were compared to those of C. trachomatis expressing BlaM alone. CT694 was included as a positive control. Error bars represent standard deviations from the means. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA. ****, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.01. (B). Data are representative of three experiments (A and B).