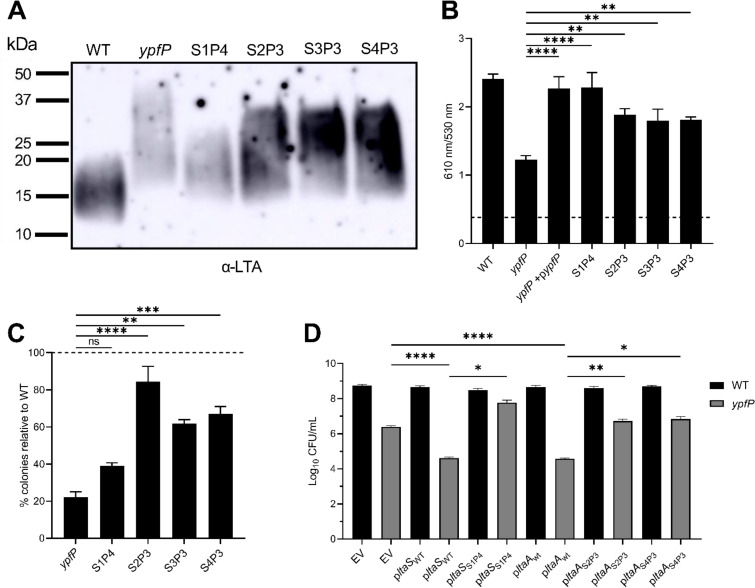
FIG 5.
Passaged ypfP mutants harbor suppressor mutations that lead to phenotypic differences in membrane potential, gentamicin resistance and LTA. (A) Immunoblot of LTA isolated from cells grown aerobically to late exponential phase. Passaged ypfP mutants are named to reflect the lineage number and the passage at which they reached viability equal to that of the WT. For example, S1P4 represents passaged lineage 1, which reached WT-like viability after four passes under anaerobic conditions. (B) Anaerobic membrane potential was measured using the fluorescent dye DiOC2. Data are means from three independent experiments performed in technical triplicate. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. ****, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.01. (C) Percent gentamicin-resistant colonies relative to the WT (dotted line). Data represent 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.001. (D) Strains were serially diluted, spot plated onto TSA, and incubated anaerobically and CFU were enumerated for the WT and the parental ypfP mutant complemented with empty pOS (EV), WT ltaS or ltaA (ltaSWT and ltaAWT), mutated ltaS from S1P4 (ltaSS1P4), or mutated ltaA from S2P3 or S4P3 (ltaAS2P3 and ltaAS4P3). Data are means from 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean. Significance was determined using a two-tailed t test. ****, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.