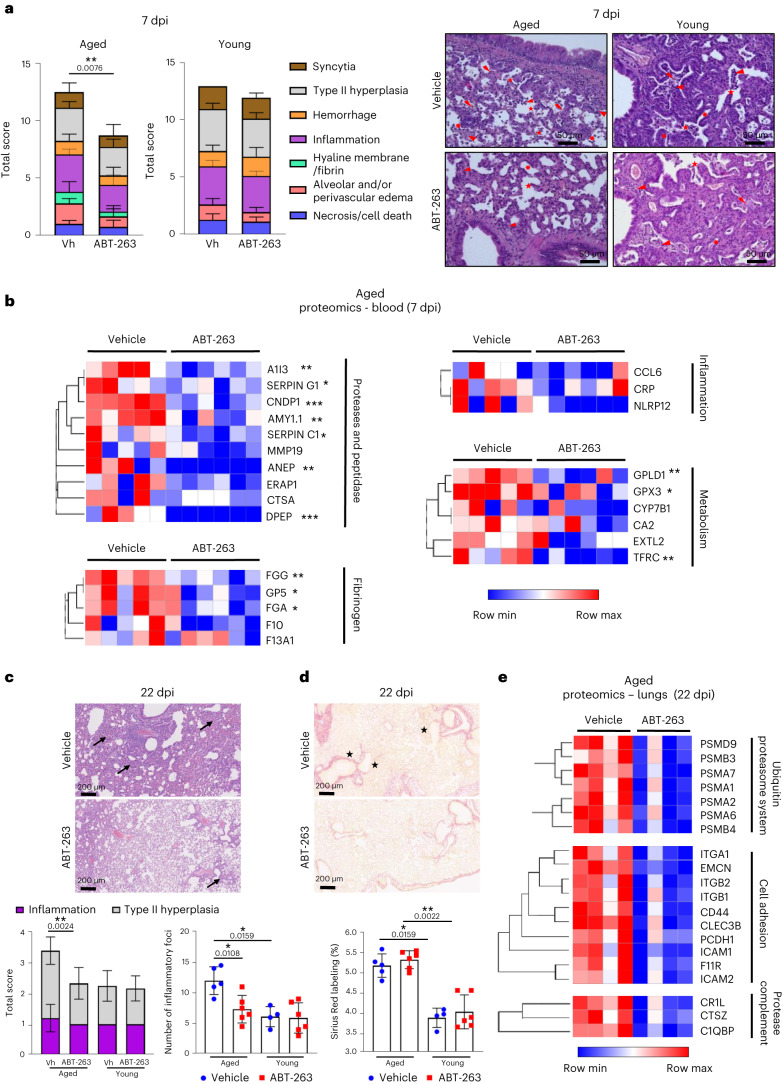
Fig. 5. Effect of ABT-263 treatment on pulmonary and systemic inflammation in aged hamsters.
Aged hamsters and young hamsters were treated (or not) with ABT-263 and then infected with SARS-CoV-2. Animals were euthanized at 7 dpi and 22 dpi. a, Left: histopathological examination of lung sections (H&E staining, 7 dpi). The sum of the subscores is shown (n = 11–12 aged and n = 6 young). Right: photomicrographs showing lower alveolar destruction in ABT-263-treated aged hamsters (but not ABT-263-treated young hamsters). Arrowhead: inflammatory cell infiltrate; star: alveolar wall rupture; sun: type II pneumocyte hyperplasia; thunderbolt: necrosis; arrow: activated blood vessel. Scale bars, 50 μm. b, Heat maps of the differential expressed prothrombotic and inflammatory factors in the serum of vehicle-treated and ABT-263-treated aged hamsters, in a mass spectrometry analysis of the proteome (fold change in protein level > 1.2, P < 0.05) (n = 5–6). c, Histopathological examination of lung sections (H&E staining, 22 dpi). Lower panels: The total histology score (left) and the numbers of inflammatory foci (inflammation and type II hyperplasia) per lung section (right) are shown (n = 4–6). d, Sirius Red labeling in the lungs of vehicle-treated and ABT-263-treated aged hamsters and young hamsters at 22 dpi. Top: representative images showing (stars) the destructured basal membranes in vehicle-treated aged animals. Bottom: the percentages of Sirius Red labeling are shown (n = 4–6). e, TMT-based proteomic analysis of lung extracts (vehicle-treated and ABT-263-treated aged hamsters). Heat maps of the differentially expressed components, in a mass spectrometry analysis of the proteome, are depicted (fold change in protein abundance > 2, P < 0.05) (n = 4). For all graphs, errors indicate mean ± s.d. Pooled results from two independent experiments (a, left) and one of two representative experiments (a, right, and b–e) are shown. Significant differences were determined using the two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test (a,b,e) and one-way ANOVA Kruskal–Wallis test (non-parametric), followed by Dunn’s post test (c,d). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.