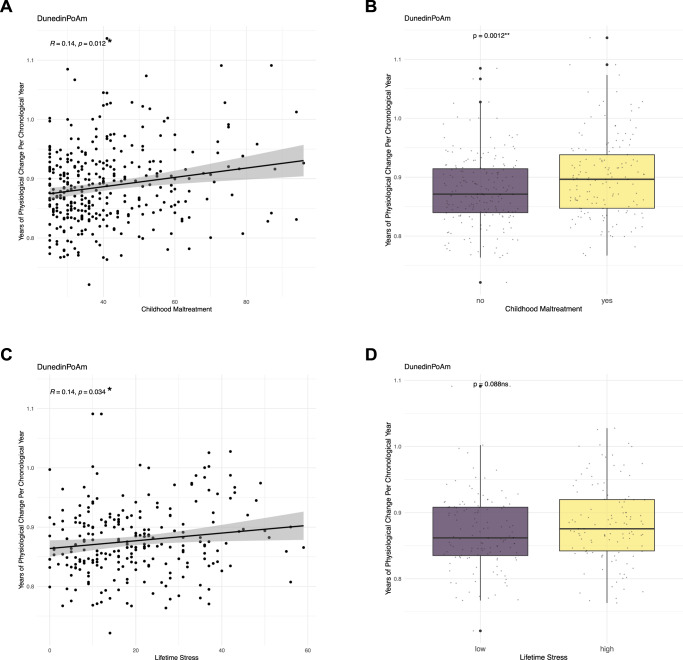
Fig. 3. Associations between DunedinPoAm and childhood maltreatment or lifetime stress.
Spearman correlation between DunedinPoAm (years of physiological change per chronological year) (A, C) on the y-axis and childhood maltreatment measured by CTQ score or cumulative lifetime stress measured by MEL score on the x-axis (Spearman correlation coefficient, rs). B displays a box plot and a p-value from a t-test of dichotomized childhood maltreatment status – abused (N = 149) vs. not abused (N = 191). The status abused was given if participant had moderate or severe abuse in any of the subscales of the questionnaire. Data was missing for 80 participants. D displays a box plot and a p-value from a t-test of dichotomized cumulative lifetime stress status – low (N = 128) vs. high (N = 115) lifetime stress categorized by the median score of the participants (median=18). This questionnaire was only available in the BeCOME cohort and was missing for 56 participants. ****P ≤ 0.0001; ***p ≤ .001; **p ≤ .01, *p ≤ .05. ns not significant.