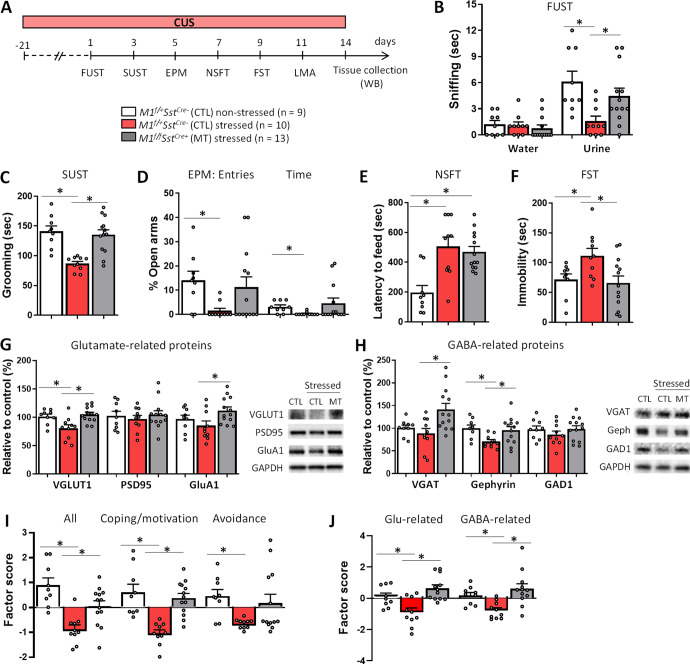
Fig. 5. M1R deletion in SST interneurons promotes stress resilience and prevents glutamate- and GABA-related protein deficits in the mPFC of M1f/fSstCre+ mice.
A M1f/+SstCre- control (CTL) and M1f/fSstCre+ mutant (MT) mice were exposed to the chronic unpredictable stress protocol (CUS) and underwent behavioral testing. B Effects of CUS on stress-related behaviors in M1f/fSstCre+ mice, including the female urine sniffing test (FUST, urine: F2,29 = 5.55, p < 0.05; water: F2,29 = 0.37, p > 0.05), C sucrose splash test (SUST, F2,29 = 14.31, p < 0.05), D elevated plus-maze (EPM, entries: H2 = 6.72, p < 0.05; time: H2 = 6.96, p < 0.05), E novelty-suppressed feeding test (NSFT, F2,29 = 10.98, p < 0.05) and F forced swim test (FST, F2,29 = 4.59, p < 0.05). G Western blotting for proteins relevant to glutamatergic signaling, including VGLUT1 (F2,29 = 7.74, p < 0.05), PSD95 (F2,29 = 0.31, p > 0.05) and GluA1 (F2,29 = 3.61, p < 0.05), H or GABAergic signaling, including VGAT (H2 = 7.15, p < 0.05), gephyrin (F2,29 = 4.74, p < 0.05) and GAD1 (F2,29 = 0.85, p > 0.05). I Data from behavioral tests following CUS exposure were grouped into Coping Strategies and Motivated Behaviors (FUST, SUST and FST) or Innate Avoidance (EPM and NSFT), and then transformed into factor scores by principal component analysis (All: F2,29 = 13.70, p < 0.05; Coping: F2,29 = 15.50, p < 0.05; Avoidance: H2 = 5.66, p < 0.05). J Factor analysis of CUS effects on glutamate- (F2,29 = 10.62, p < 0.05) and GABA-related proteins (F2,29 = 6.12, p < 0.05) in M1f/fSstCre+ mice. *p ≤ 0.05 compared to the control group; One-way ANOVA followed by Duncan test (F value, normal distribution) or Kruskal–Wallis followed by Dunn’s test (H value, non-normal distribution).