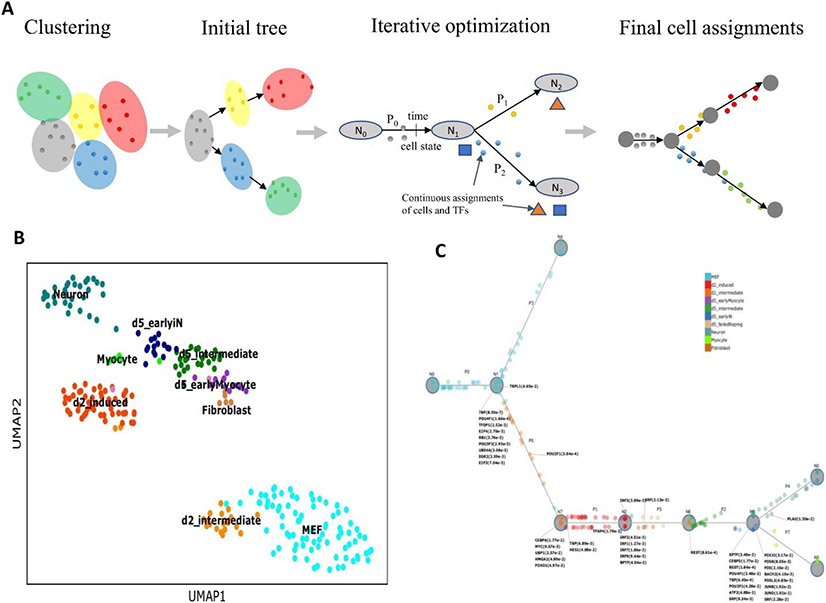
Figure 3. Dynamic regulatory network inference using CSHMM.
a ∣ A scheme for continuous-state hidden Markov model (CSHMM) and cell assignment learning. The method is initialized using clustering in gene space. Relationships between clusters are analyzed to obtain an initial branching model. Next the method iterates between cell assignment along the branches of the branching model and learning model parameters including structure and emission probabilities. Cell assignment is also determined based on predicted transcription factors (TFs) for each branching point and their targets allowing the method to infer key TFs and their activation time. b ∣ A Standard uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plot of cells profiled to study neuron differentiation73. c ∣ CSHMM reconstructed trajectory for the same cells. Cells are assigned to different locations along the branches based on their inferred pseudotime. The model also includes parameters for the expected expression levels for all genes at each time. Key TFs and their p-values are associated with each of the branching points in the model.