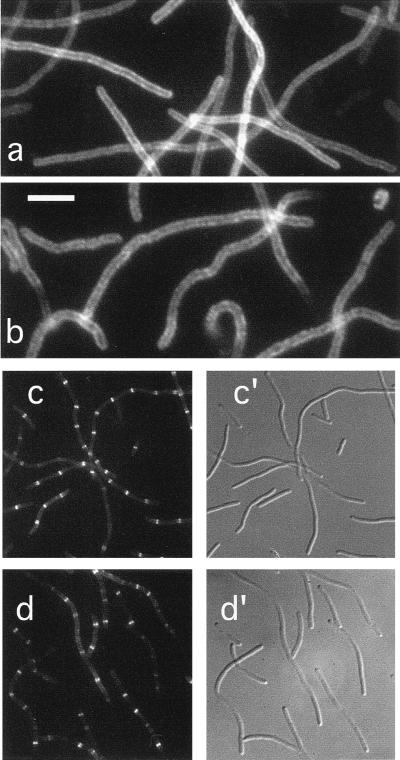
FIG. 4.
Localization of ZipA in FtsZ− and FtsA− filaments. Fluorescence (a to d) and differential interference contrast (c′ to d′) micrographs showing the location of ZipA-Gfp (a and c) or native ZipA (b and d) in filaments depleted for FtsZ (a and b) or FtsA (c and d). Cells shown are from the FtsZCID strain PB143(λCH50)/pDB346 [ftsZ0(Plac::zipA-gfp)/cI857 PλR::ftsZ+] (a), the FtsZHID strain PB143/pCX41 [ftsZ0/repA(Ts) ftsZ+] (b), the FtsACID strain CH2(λCH50)/pDB355 [ftsA0(Plac::zipA-gfp)/cI857 PλR::ftsA+] (c), and the FtsAHID strain CH2/pDB280 [ftsA0/repA(Ts) ftsA+] (d). Cells in panels b and d were grown at 42°C prior to staining with affinity-purified anti-ZipA antiserum. Cells in panels a and c were grown at 30°C in the presence of 25 μM IPTG and were observed immediately after chemical fixation. Bar represents 5.0 (a and b) or 11.7 (c and d) μm.