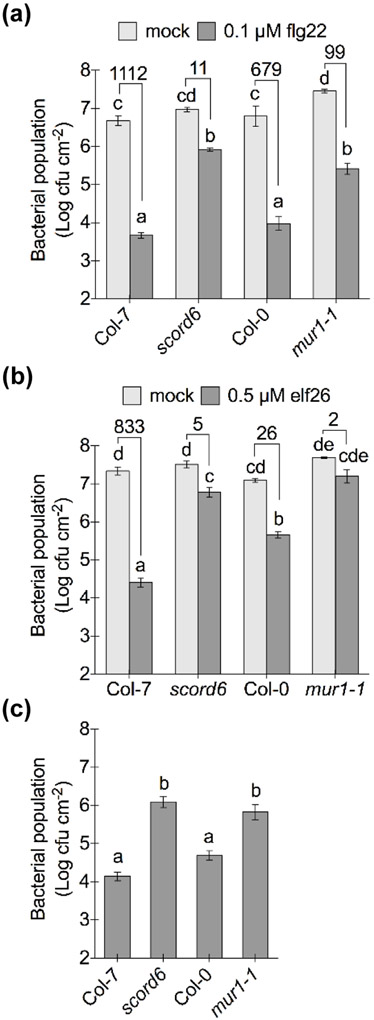
Fig. 3: Mutations in the MUR1 gene affect flg22-, elf26- and AvrRpt2-induced immunity in Arabidopsis.
(a) Bacterial populations two days after infiltration-inoculation with 1 × 106 cfu ml−1 Pst DC3000. Plants were pre-treated with 0.1 μM flg22 or 0.1% DMSO (mock) for 22 hours. Different letters above columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) between bacterial populations (n = 4, error bars, ± SEM); analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. Numbers above the columns are fold changes of bacterial populations with flg22 treatment compared to mock treatment, indicating the inhibition of bacterial growth with flg22 treatment.
(b) Bacterial populations two days after infiltration-inoculation with 1 × 106 cfu ml−1 Pst DC3000. Plants were pretreated with 0.5 μM elf26 or 0.1% DMSO (mock) for 22 hours. Different letters above columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) between bacterial populations (n = 4, error bars, ± SEM), analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. Numbers above the columns are fold changes of bacterial populations with elf26 treatment compared to mock treatment, indicating the inhibition of bacterial growth with elf26 treatment.
(c) Bacterial populations two days after infiltration-inoculation with 1 x 106 cfu ml−1 Pst DC3000 (avrRpt2). Different letters above columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) of bacterial population between plant genotypes (n = 4, error bars, ± SEM); analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test.