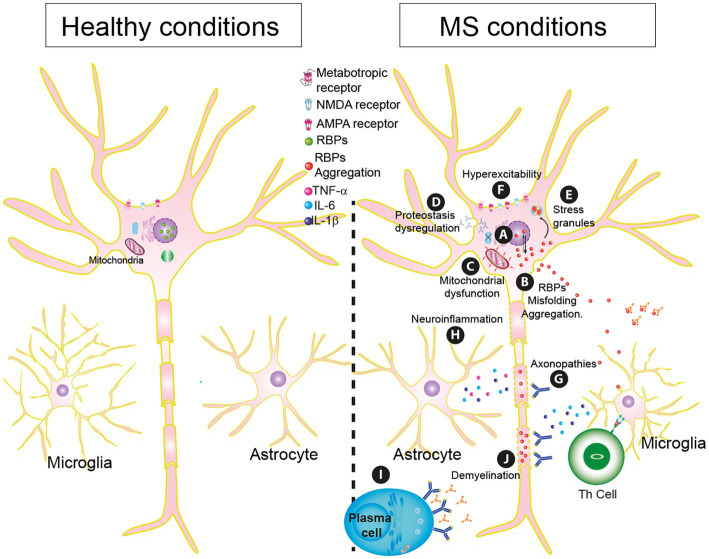
Figure 2.
Essential pathophysiology mechanisms in Multiple sclerosis (MS). (A) RBP mislocalization by cellular stressors. (B) RBPs dysfunctionality: misfolding, and aggregation. (C) Mitochondrial dysfunction. (D) Proteostasis dysregulation. (E) Generation of stress granules. (F) Hyperexcitability. (G) Axonopathies. (H) Neuroinflammation. (I) Plasma Cells. (J) Demyelination.