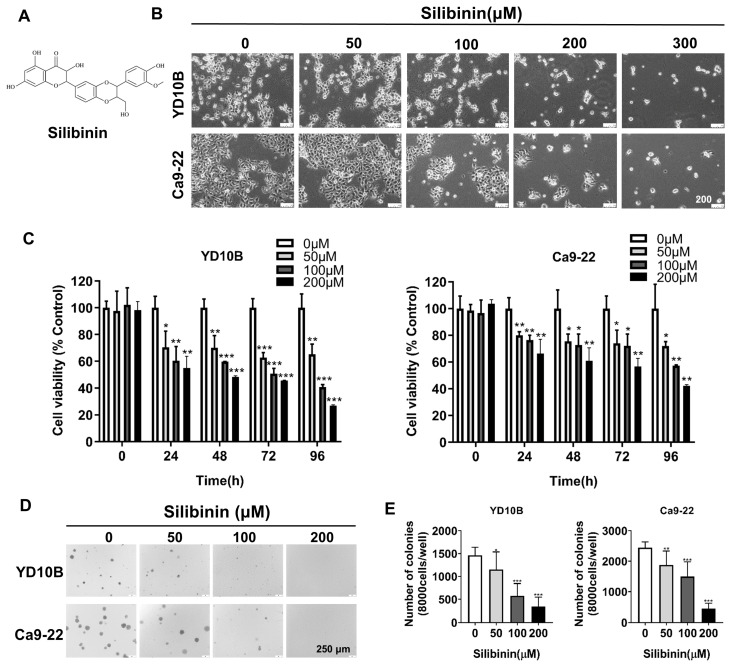
Figure 1.
Silibinin inhibits oral cancer cell growth. (A) Chemical structure of silibinin. (B) Morphology of YD10B and Ca9-22 cells after treatment with the indicated concentrations of silibinin for 48 h observed under a light microscope (magnification, 100×). (C) YD10B and Ca9-22 cells were treated with 0, 50, 100, and 200 μM silibinin for 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. Cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assay. (D) Effects of silibinin on colony formation in YD10B and Ca9-22 cells (magnification, 50×). *p<0.05; ** p< 0.01; *** p< 0.001.