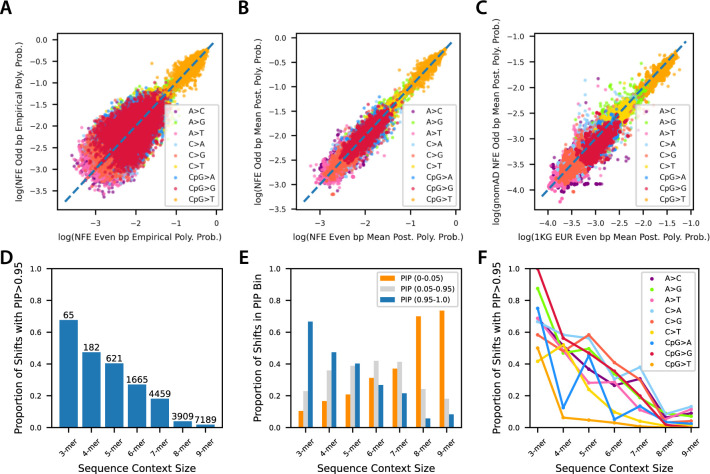
Fig 3. Baymer model validation, transferability, and regularization in gnomAD non-Finnish European (NFE) polymorphisms with derived allele count greater than or equal to two in non-coding accessible regions.
(A) Empirical 9-mer polymorphism probabilities for context mutations with at least one occurrence in both datasets (15,910 omitted context mutations) are plotted against one another (Spearman correlation = 0.915; p < 10−100; RMSPE = 0.12). (B) Baymer mean posterior estimates for 9-mer polymorphism estimates in even and odd base pair datasets (Spearman correlation = 0.990; p < 10−100; RMSPE = 0.035). (C) Baymer mean posterior estimates for 9-mer polymorphism estimates in odd base pair non-Finnish European gnomAD data and even base pair NYGC 1KG phase three data, down-sampled to match total number of polymorphisms and site frequency spectrum (Spearman correlation = 0.984; p < 10−100; RMSPE = 0.045). (D) Fraction of edges in the NFE model with a PIP > 0.95 in each sequence context window layer. Absolute count of edges above bars. (E) For high-data contexts with at least 100,000 total instances in the non-coding genome and 50 total mutations, fraction of edges at each sequence context window size across PIP bins. (F) Proportion of high-data contexts within each mutation type at each sequence context window size with PIP>0.95.