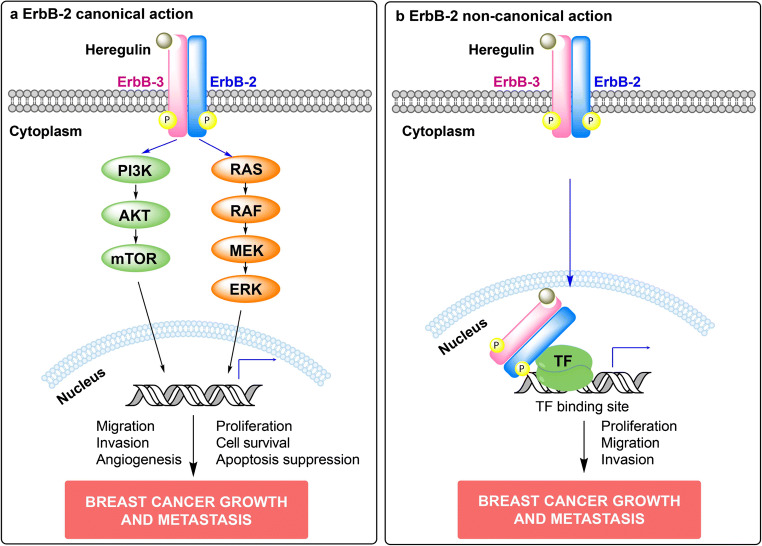
Fig. 1.
Canonical and non-canonical actions of ErbB-2 in breast cancer (BC). a ErbB-2 canonical signaling pathway. Upon ligand binding, ErbBs form homodimers or heterodimers, which activate downstream signaling cascades and transduce ErbBs effects. Heregulin-induced ErbB-2/ErbB-3 heterodimers are illustrated. The two key signaling pathways activated are p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT. Activation of the MAPK pathway leads to the transcription of genes that drive cellular proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis, while activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway leads to downstream cellular endpoints including cell survival and apoptosis suppression (reviewed in [17]). Altogether, activation of these signaling cascades promotes BC growth and metastasis. b ErbB-2 non-canonical action. ErbB-2 non-canonical action involves nuclear translocation of membrane ErbB-2. Heregulin-induced ErbB-2/ErbB-3 heterodimerization and nuclear translocation is depicted [19]. Once in the nucleus, ErbB-2 may directly bind to its response elements and function as a transcription factor (TF), or may tether to other TFs and act as a transcriptional coactivator. An example of ErbB-2 acting as a transcriptional coactivator is shown. NErbB-2 actions also drive BC growth and metastasis