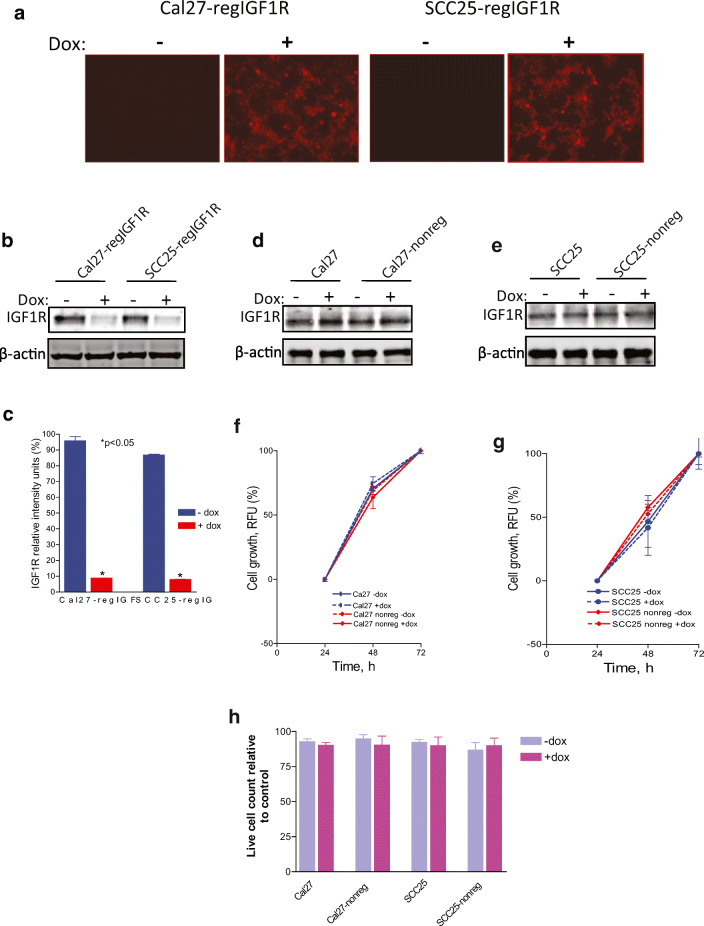
Fig. 1.
Induction of shRNAmir-IGF1R with doxycycline reduces IGF1R expression. Indicated cell lines were grown in the absence or presence of 2 μg/ml doxycycline for 3 days. Cal27 and SCC25, parental cell lines. Cal27-regIGF1R and SCC25-regIGF1R, cell lines transfected with IGF1R-pTRIPZ-shRNAmir. Cal27-nonreg and SCC25-nonreg, cell lines transfected with non-silencing pTRIPZ-shRNAmir (negative control). a Fluorescence microscopy demonstrates expression of the reporter TurboRFP in the presence of doxycycline. b Representative immunoblot demonstrating regulation of IGF1R expression by doxycycline. c Quantification of densitometric analysis of three such immunoblots showing relative intensity of IGF1R band normalized to β-actin band. d, e Representative immunoblots demonstrating no impact of doxycycline or negative control plasmid on IGF1R expression. f, g Parental Cal27, Cal27-nonreg, SCC25, and SCC25-nonreg cells were grown in 96-well plates in the absence or presence of 2 μg/ml doxycycline as indicated. Proliferation was measured using the alamarBlue assay at 24, 48, and 72 h. Data are expressed as net fluorescence. Values represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate and demonstrate no effect of non-silencing shRNAmir expression or dox treatment. h Cell viability by trypan blue assay at 72 h. Data are expressed as average live cell counts ± SEM for three independent experiments performed in triplicate. No effect of non-silencing shRNAmir expression or dox treatment. Asterisk indicates significant difference between −dox and +dox, p < 0.05