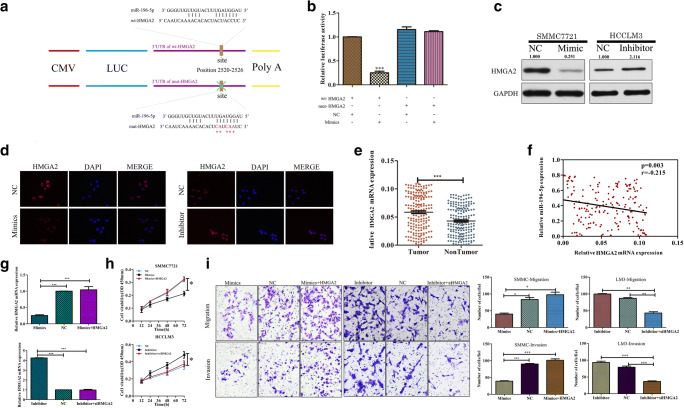
Fig. 4.
miR-196-5p targets HMGA2 to modulate HCC biology. The wild-type (wt) and mutated (mt) versions of the putative miR-196-5p binding site in the HMGA2 3′UTR are shown and were generated. b WT construct luciferase activity was markedly suppressed by miR-196-5p overexpression, whereas the mutant construct activity was unaffected in SMMC7721 cells. c Overexpression and inhibition of miR-196-5p expression markedly reduced and increased HMGA2 protein levels in SMMC and HCCLM3 cells, respectively. d HMGA2 expression as assessed via immunofluorescent microscopy. (Original magnification, × 400). e Comparison of HMGA2 expression in HCC tumor samples and adjacent controls, with GAPDH used for normalization. f A negative correlation between expression of HMGA2 and miR-196-5p in HCC tumors. (g, upper) Measurement of HMGA2 expression in SMMC7721 cells transfected with miR-196-5p mimics with or without an HMGA2 or control vector. (g, lower) Measurement of HMGA2 expression in cells expressing miR-196-5p inhibitors with or without siHMGA2 or control vectors. h CCK8 assays were conducted using SMMC7721 cells overexpressing miR-196-5p that were or were not transfected with HMGA2 or control vectors, as well as using HCCLM3 cells transfected using a miR-196-5p inhibitor with or without an siHMGA2 or control vector. i Transwell assays revealed that overexpression of HMGA2 was able to reverse the ability of miR-196-5p to inhibit HCC migration and invasion in SMMC cells, whereas knockdown of HMGA2 had the opposite effect in LM3 cells (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)