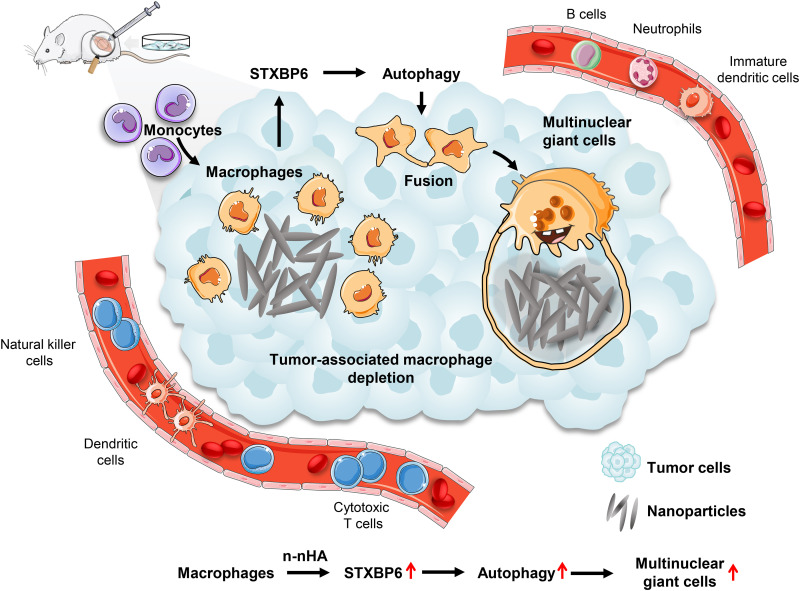
Fig. 6. Schematic illustration of the antitumor immunity evoked by n-nHA.
The intervention of n-nHA countered tumor-mediated inflammation and engineered an antitumor immune microenvironment mitigating tumor growth. n-nHA injected intratumorally into tumor-bearing mice effectively promoted the fusion of macrophages to form substantial MNGCs surrounding the nanoparticle aggregates. This considerable fusion event of macrophages resulted from the elevated expression of STXBP6 induced by n-nHA, followed by the activation of macrophage autophagy. Through the formation of MNGCs, n-nHA induced extensive depletion of tumor-associated macrophages and permitted more tumor-killing immunocytes, including cytotoxic T cells, DCs, and NKs, to infiltrate into the TME, which notably impaired tumor progression.