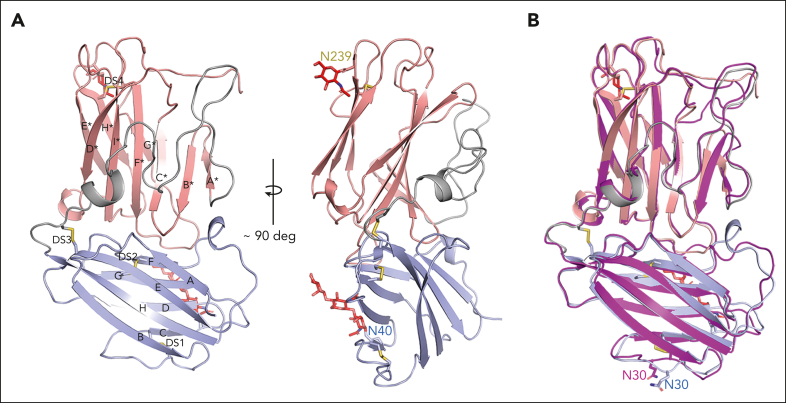
Figure 2.
The crystal structure of lufaxin. (A) The N-terminal domain is colored light blue and C-terminal domain, copper. In the left-hand structure, β-strands of the N-terminal domain are labeled A-G, and β-strands of the C-terminal domain are labeled A∗-H∗. Cysteine residues are shown as sticks, with sulfur atoms colored yellow. Disulfide bonds (DS1-DS4) are labeled (left). Visible glycan chains are colored red, and their positions of attachment (Asn 40 and Asn 239) are labeled (right). (B) Superposition of the lufaxin crystal structure with the structure predicted by Alphafold2 (magenta). The overall structures are very similar (root mean squared deviation = 0.69 Å for 227 Cα atoms), but they differ in the backbone conformation of loop B-C, which interacts with the C3bB complex (see "Cryo-EM studies of the C3bB-lufaxin complex").