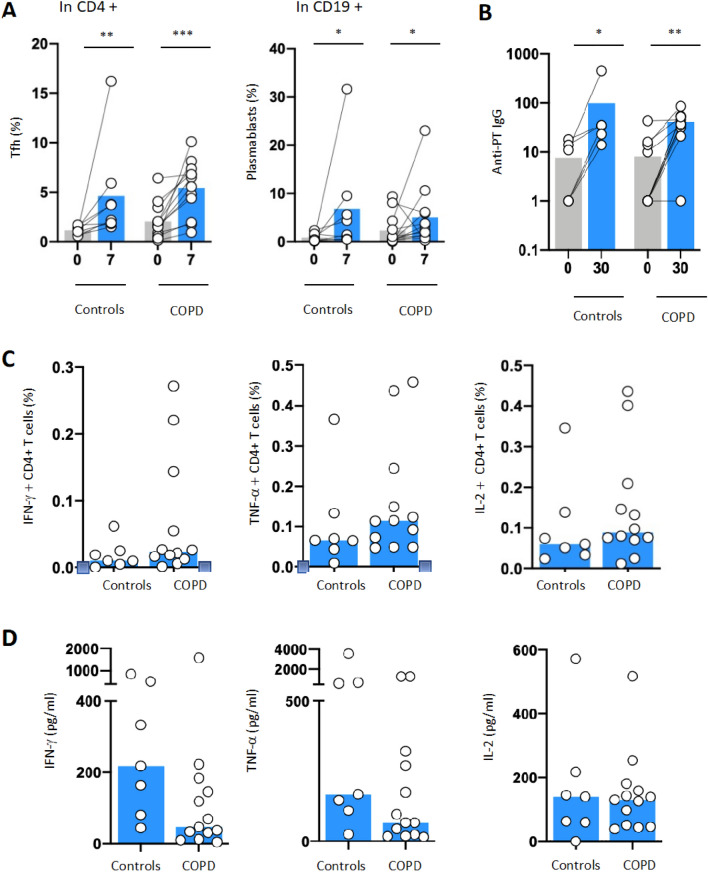
Figure 1.
Humoral and cellular responses to Bordetella pertussis stimulation in patients with COPD compared to controls. To measure immune responses to Pertussis vaccine, blood from n = 8 control donors and n = 13 patients was withdrawn at baseline and at day 7 or 28 days upon vaccination. (A) TFH cells (CD3+ CD4+ CXCR5+ PD1+) and plasmablasts cells (CD19+ CD38+) were measured by flow cytometry (LSRII, BD Biosciences), at baseline (D0) and 7 days (D7) after pertussis vaccination in COPD patients (n = 12) and controls (n = 8). (B) Anti-pertussis circulating immunoglobulin G (anti-PT IgG) antibodies were measured using enzyme immunoassay at D0 and D7 in COPD patients (n = 11) and controls (n = 6) (Biomnis). (C) T cell specific responses were monitored with intracellular cytokine staining for IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α following ex vivo PBMC stimulation with Bordetella pertussis peptide pool (filamentous hemagglutinin [FHA], fimbriae 2/3 [Fim2/3], pertactin [PRN], and inactivated pertussis toxin [PT]) antigens) in patients with COPD (n = 12) and controls (n = 7). (D) Concentration of IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α (pg/mL) was measured in culture supernatants from COPD patients (n = 13) and controls (n = 13) using Luminex technology following manufacturer instructions (HCYTMAG-60K-PX41). Supernatants were collected on day 5 after stimulation with Bordetella pertussis peptide. Median values are shown and statistical significance was evaluated by Wilcoxon test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.