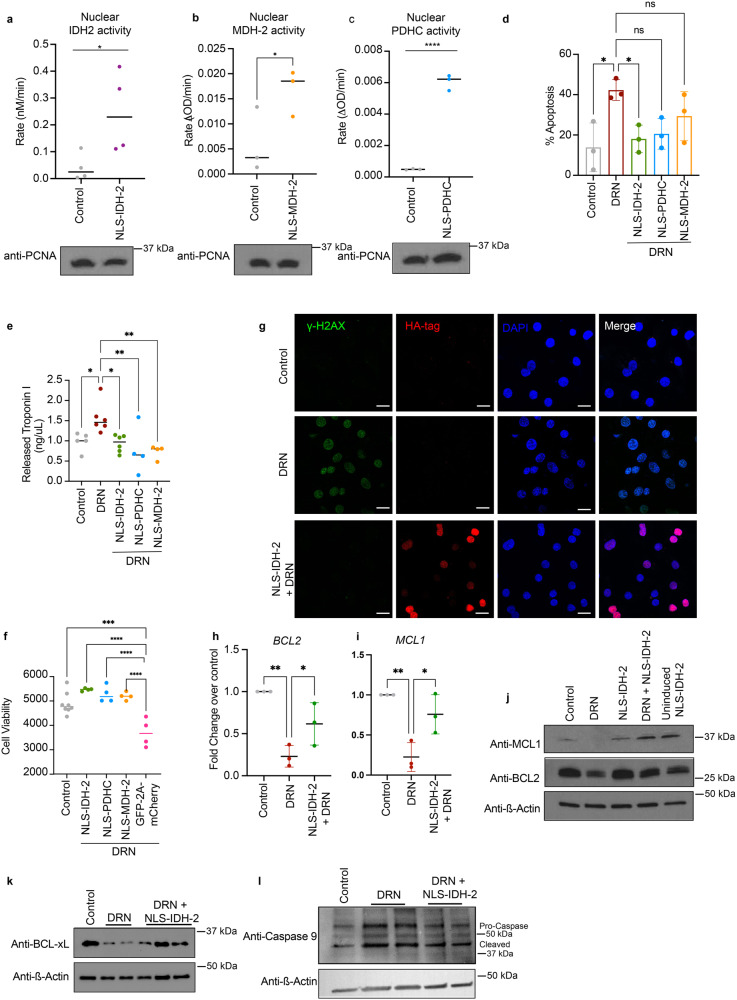
Fig. 2. Nuclear translocation of TCA cycle enzymes prevents doxorubicin-mediated cellular damage.
a–c Enzyme activity of IDH-2 (n = 4) (a), MDH-2 (n = 3) (b), and PDHC (n = 3) (c) in nuclei isolated from cells transduced with tetracycline-inducible NLS-IDH-2 constructs. Activity is represented as the rate in nM/min or ΔOD/min, p value* <0.05, p value**** = 0.0001, and lysates were probed for PCNA to detect equal nuclear protein amounts used for the assay. d Reduced apoptotic cell death as measured by Annexin:V:FITC staining in cells expressing nuclear TCA cycle dehydrogenases prior to doxorubicin DRN treatment. N = 3 p value* <0.05 (e) Quantification of troponin I released from cardiomyocytes as a marker of cardiac injury, minimum n = 4 p value** <0.007, p value* <0.05. f Cell death as measured by Cell Titer GloTM in cells expressing nuclear dehydrogenases prior to DRN treatment. minimum n = 4 p value*** = 0.0001, p value**** <0.0001. NLS-EGFP-2A-NLS-mCherry was used as a control for the 2 A linker system. g DNA damage as assessed by ɣ-H2AX foci formation. Scale bar 20 µm. h, i qRT‒PCR showing the expression of anti-apoptotic genes BCL2 (h) and MCL1 (i). n = 3 P value ** <0.005, *<0.05. j–l Protein levels of anti-apoptotic proteins (j, k along with reduced caspase 9 cleavage (l) in cells expressing nuclear IDH-2 compared to cells treated with doxorubicin.