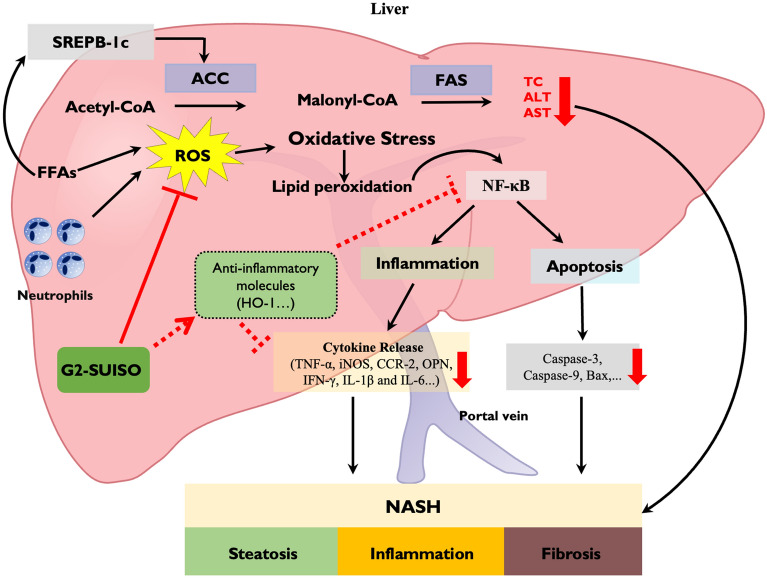
Figure 5.
Schematic hypothesis of the mechanisms underlying the effects of G2-SUISO for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The beneficial effect of G2-SUISO against hepatic steatosis in NASH elderly rats may occur through the inhibition of lipogenesis pathways by reducing SREBP-1c, ACC and FAS gene expression, thereby causing a reduction in the hepatic fat accumulation and a significant decrease in total cholesterol (TC) levels in serum. The administration of G2-SUISO can decrease lipid peroxidation and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, iNOS, CCR-2, IFN-γ, OPN, IL-1β and IL-6, which modulate liver damage in CDHCFF diet-fed rats. G2-SUISO might also up-regulated anti-inflammatory molecules, such as HO-1, which suppressed NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine expression. G2-SUISO is therefore able to reduce the activities of AST and ALT in the serum of NASH elderly rats. Furthermore, G2-SUISO was found to exert anti-apoptotic effects as well by down-regulating pro-apoptotic molecules, such as caspase-9, caspase-3 and Bax via down-regulation of NF-κB. Overall, this study provides evidence for the beneficial effects of G2-SUISO in reversing the progression of NASH in elderly rats.