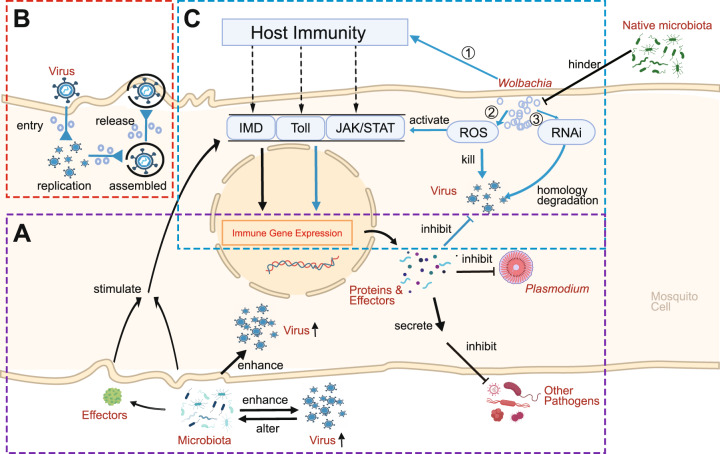
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of the microbiota-mosquito-pathogen interactions.
A The mosquito microbiota modulates mosquito pathogen infection by stimulating host immune signal regulation or secreting effectors, or by enhancing intracellular/extracellular viral infection through different mechanisms. Meanwhile, viral infection can alter the composition of the mosquito microbiota. B Wolbachia induces a PB effect by disrupting or competing for cellular cholesterol and lipid homeostasis in viral infection. C Wolbachia induces a PB effect by stimulating mosquito immunity. (1) Wolbachia activates the IMD, Toll, and JAK/STAT pathways to increase the expression of downstream effectors. (2) Wolbachia directly kills pathogens through the ROS pathway, which may participate in other immune processes. (3) Wolbachia induces homology degradation of viral RNA by the RNAi pathway. Blue arrows: the process of a Wolbachia-induced PB effect mediated through mosquito immunity; Blue arrows with a triangle (in box B): Wolbachia-induced PB in viral transmission. Black arrows: other microbiota-induced pathogen inhibition.