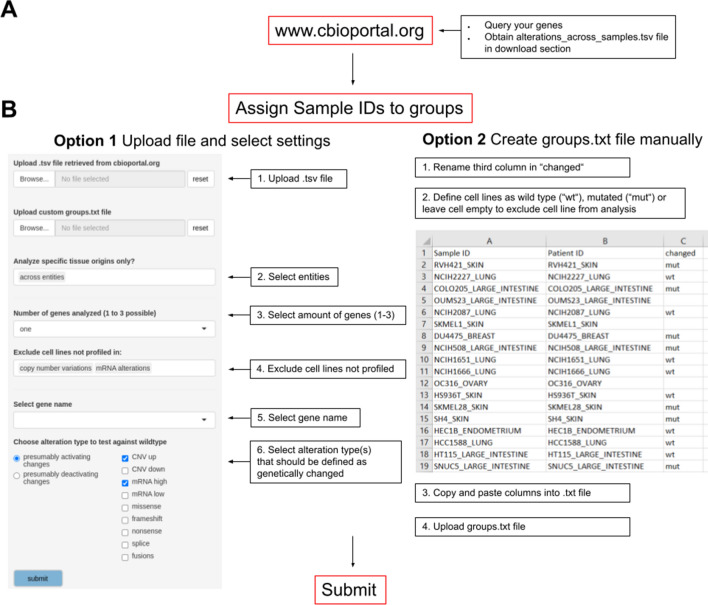
Fig. 2.
Step-by-step user workflow. A Obtain genetic alterations of query genes in the ‘alterations_across_samples.tsv’ file from www.cBioPortal.org as described at https://tools.hornlab.org/GDSC/Manual.pdf and in Supplementary Fig. 1–2. B Based on this file, cell lines are classified in ‘genetically changed’ and ‘wild type’ as reference. Option 1: tumor entities (tissue origins) of interest can be selected. Up to three genes can be chosen for analysis. The webtool provides automated assignment of cell lines into groups, by default ‘presumably activating’: amplifications (CNV up), high mRNA as defined by cBioportal. Default: ‘presumably deactivating’: homozygous deletions (CNV down), low mRNA, nonsense- and frameshift mutations. Users can additionally select missense mutations, splice variants and gene fusions. For two or three genes, cell lines can be defined as ‘mutated’ if at least one of the genes is changed or optionally, if all genes are changed (co-mutation). Option 2: custom grouping based on a tab-delimited text file and used in the upload option of the webtool. It should contain 3 columns named ‘Sample.ID’, ‘Patient.ID’, and ‘changed’. The first two columns are retrieved from the ‘alterations_across_sample.tsv’ file and the third column, added by the user, defines the cell lines as ‘mut’ for mutated/genetically changed and ‘wt’ for wild type (empty cells to exclude cell lines)