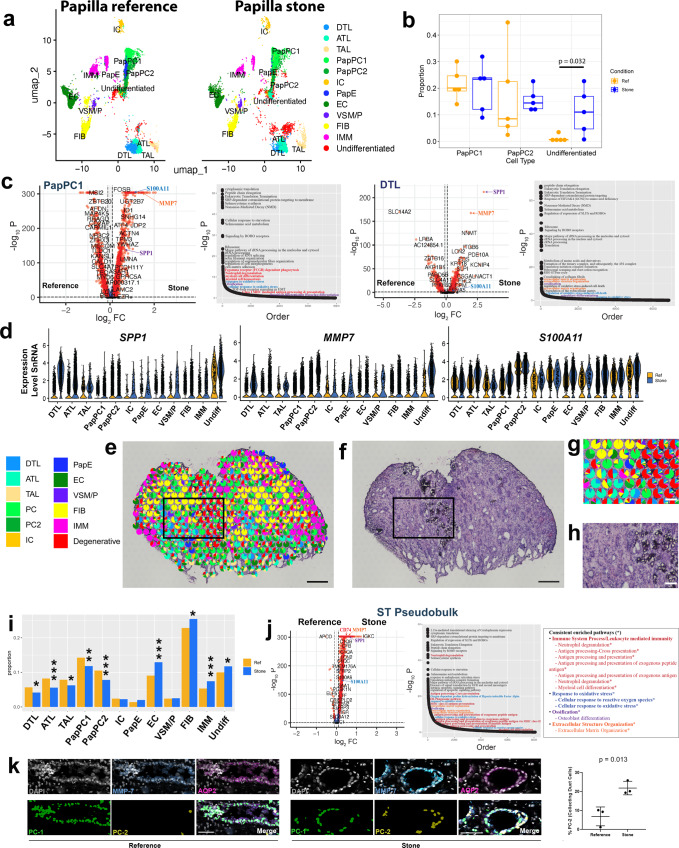
Fig. 3. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and cell states induced by stone disease within the human papilla.
a UMAPs display cell types clustered from snRNA sequencing in papillary reference and stone samples, highlighting the expansion of the undifferentiated cell population in stone disease. b Proportion of PapPC1, PapPC2 and undifferentiated cell types for each specimen (n = 5 stone and n = 5 reference independent papillary specimens), validated the expansion of the undifferentiated population (box plots display median and interquartile range; two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test was used). c DEGs (two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test) and enriched pathways (overrepresentation test, see methods) in papillary cells by snRNAseq, focusing on PapPC1 and descending thin limbs (DTL, a cell important in stone disease pathogenesis). DEGs for other cell types are shown in Supplementary Figs. 10–11. Pathway analysis detected significant upregulation of ossification (purple), extracellular matrix organization (orange), response to oxidative stress (blue) and immune system process /leukocyte activation pathways (red text). d Expression of SPP1, MMP7 and S100A11 are consistently induced in stone disease across papillary cell types. e Label transfer of cell classes onto spatial transcriptomic spots in a stone disease papilla with underlying H&E histology (f). g An enlarged area from (e and f) showing the undifferentiated cell signature localizing to areas of mineralization (h). The distribution of cell signatures (percent of total spots for reference vs stone disease) in ST specimens is shown in (i). *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001 and ***p < 0.0001 (two-tailed Fisher’s exact test). j DEGs between pseudobulk (combined gene expression of spots) of reference (left) and CaOx stone ST samples (two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test). Differentially enriched pathways (overrepresentation test) in stone disease are illustrated in the pathway curve. Consistently enriched pathways that were common in each individual sample (N = 6) compared to reference samples (N = 4) are listed. k Analysis of MMP7 protein expression using 3D imaging and tissue cytometry (N = 3 reference and N = 3 stone specimens), showing a higher proportion of MMP7 high cells (PapPC2) within collecting ducts in stone disease vs. reference (mean ± standard deviation (error bars); p = 0.041 -unpaired two-tailed t-test). Scale: e, f = 300 µm; g, h = 100 µm; k = 10 µm.