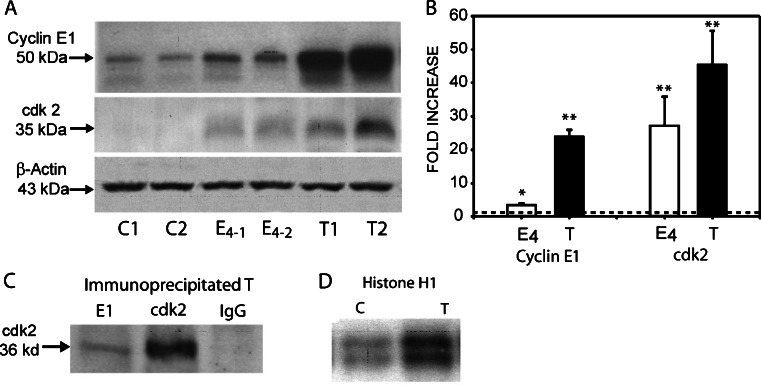
Fig. 2.
Western blot analysis of cyclin E1 and CDK2 (a, b), in vivo complex formation between cyclin E1 and CDK2 (c), and in vitro kinase activity (d). a Representative western blots of individual, age-matched, untreated control mammary glands (C1, C2), 4.0-month E2-treated mammary glands (E4-1 and E4-2), and primary tumors (T1, T2) (n = 6). b Protein expression was measured using a Molecular Dynamics PDSI with ImageQuant software and graphed as fold increase. Cyclin E1 expression increased 3.3- and 24.0-fold, after 4.0-month E2-treatment and in E2-induced tumors, respectively; while CDK2 expression increased 27.0- and 45.0-fold, respectively. β-actin was used as a loading control. c Cyclin E1 and CDK2 immunoprecipitated from E2-induced tumors and subjected to western blot analysis to determine the presence of CDK2 protein. Cyclin E1 co-immunoprecipitated with CDK2, but did not with normal rabbit IgG used as negative control. d Cyclin E1 immunoprecipitates subjected to in vitro kinase assays as described in the text. Kinase activities were higher in mammary tumors (T) than in untreated control mammary glands. Data represent the mean ± standard error. Statistical significance was determined by t test. *p < 0.04 vs control, **p < 0.001 vs control. The dotted line indicates the mean of control untreated age-matched samples.