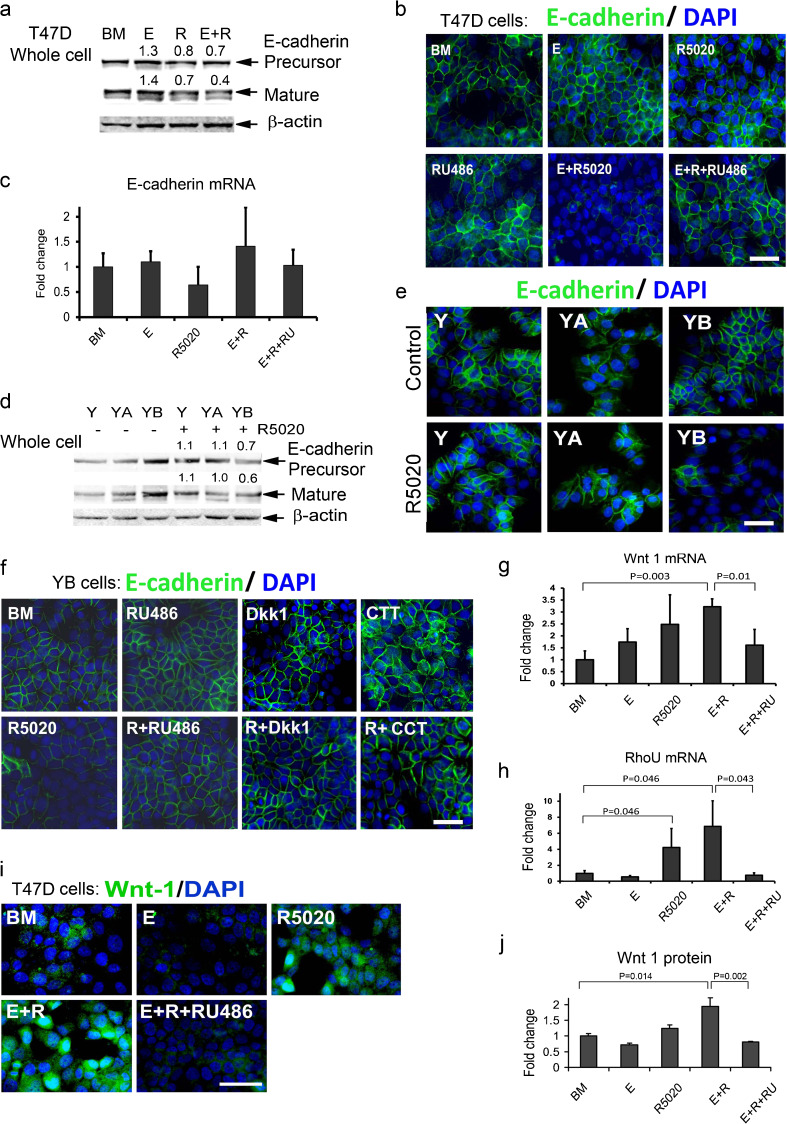
Fig. 5.
Progesterone decreases E-cadherin protein via activation of the Wnt pathway by progesterone receptor B (PRB). a T47D cells co-expressing PRA and PRB were treated with estradiol (E), R5020 (R), or E + R5020 (E + R) for 48 h and assayed by immunoblot. Numbers above bands indicate average levels of E-cadherin precursor or mature protein, respectively, compared with basal media (BM). b, c T47D cells were treated with E, R, E + R, and E + R plus progesterone receptor inhibitor RU486 for 48 h and assayed by b immunofluorescence (green cytoplasmic staining) or c processed for mRNA preparation. d, e Y, YA, and YB cells were treated with or without R5020 for 24 h and assayed by d immunoblot or e immunostaining. d Numbers above or below E-cadherin bands indicate levels compared with untreated cells for E-cadherin precursor or mature protein, respectively. f Representative images of E-cadherin immunostaining in YB cells treated with or without R5020 and with or without PR inhibitor RU486 (R + RU486) or Wnt inhibitors, Dkk1, and CCT. g-j T47D cells were treated with E, R, E + R, or E + R + RU486 for 48 h. Real-time RT-PCR analysis of g Wnt 1 mRNA or h RouU mRNA levels. The bars represent the mean ± SEM fold difference compared with mRNA levels in cells cultured in BM. i Representative images of staining with anti-Wnt 1 antibody and j quantitative analysis of Wnt 1 immunofluorescence in treated cells relative to BM. b, e, f, i Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 μm