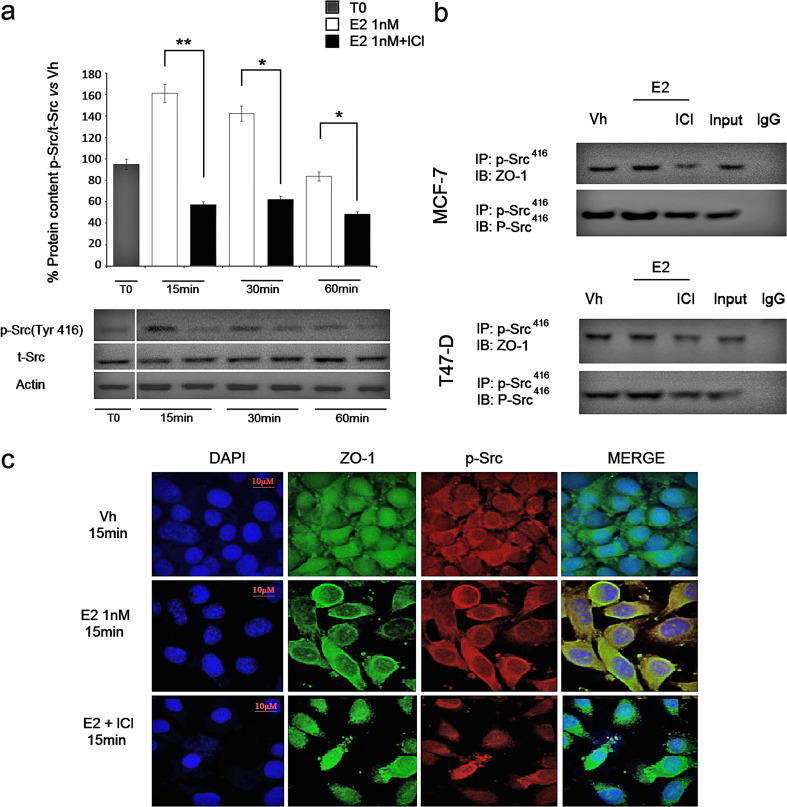
Fig. 1.
E2 activates c-Src and induces rapid formation of p-Src/ZO-1 complex in human breast cancer cells. a In MCF-7 cells, E2 (1 nM) induced a significant increase in the phosphorylation of c-Src at 416Tyr after 15 to 30 min of incubation (white bars), an effect that was precluded by the use of the ER antagonist ICI (1 μM; black bars) to values below to the initial time, where no ethanol was added (T0; gray bar). Phospho-Src416 (p-Src) densitometry values were adjusted to total Src (t-Src) intensity and then normalized to vehicle (Vh), as 100 %. *P < 0.05 vs. E2 + ICI and **P < 0.01 vs. E2 + ICI. b MCF-7 or T47D cell proteins were co-immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies against p-Src416 and ZO-1, in the absence and presence of 1 nM of E2 for 15 min, with or without ICI. The membranes were re-blotted for the immunoprecipitated protein to show equal input (left lane). Representative images of at least three independent experiments are shown. c MCF-7 cells were stained with anti-phosphor-Src and observed under confocal microscopy after 15 min of incubation with vehicle or E2, in the absences and presence of ICI. Secondary fluorescent antibodies were FITC (green) and Texas Red (red) for ZO-1 and p-Src, respectively. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Double staining (yellow signal) highlights areas of colocalization