Figure 1.
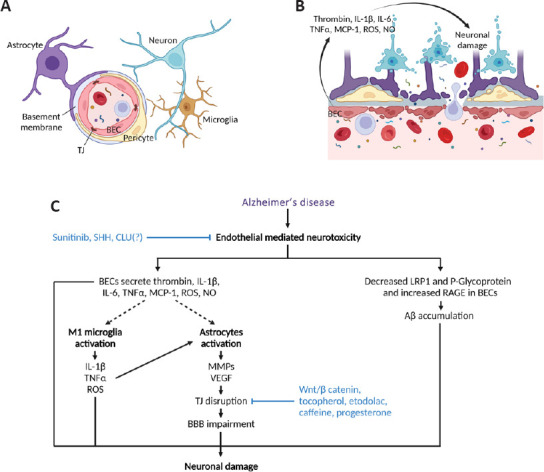
Impaired brain endothelial cells in Alzheimer’s disease.
(A) Elements of a healthy BBB include pericytes, astrocytes, basement membrane, microglia, and BECs closely linked by TJ. (B) In AD, BECs secrete proinflammatory factors that contribute to neuronal damage. (C) Diagram showing how endothelial-mediated neurotoxicity could be targeted in AD to decrease neuronal damage. Whether CLU(?) inhibits endothelial-mediated neurotoxicity remains to be determined. Aβ: Amyloid beta; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; BBB: blood-brain barrier; BEC: brain endothelial cell; CLU: clusterin; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; LRP1: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MMPs: metalloproteinases; NO: nitric oxide; RAGE: receptor for advanced glycation endproducts; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SHH: sonic hedgehog; TJ: tight junction; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor α; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; Wnt: wingless and Int-1. Created with BioRender.com.
