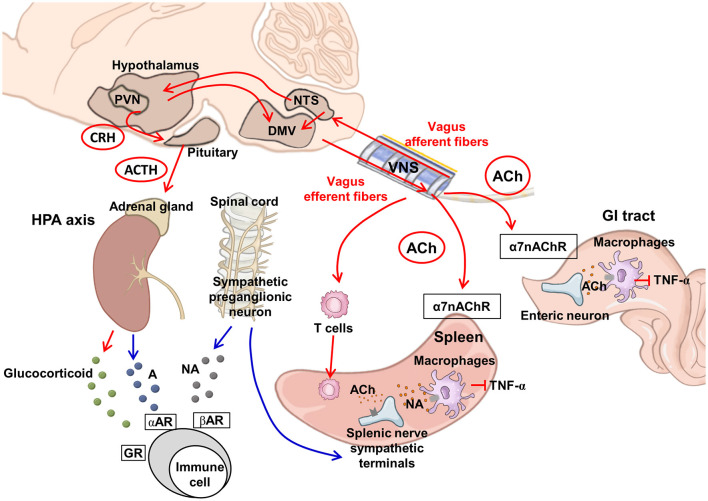
Figure 1.
Proposed neuroimmunomodulation by vagus nerve stimulation. VNS can activate vagal afferent fibers projecting to the NTS, which relays to the PVN in the hypothalamus and DMV. The DMV transmits downward signals via vagal efferent fibers. The PVN activates the HPA axis, releasing glucocorticoids from the adrenal glands to exert an anti-inflammatory effect (Berthoud and Neuhuber, 2019). The sympathetic preganglionic neurons project to the splenic nerve. The splenic nerve sympathetic terminals can be modulated by ACh via the vagus-to-spleen circuit. In addition, the activation of ACh-synthesizing T cells can stimulate the sympathetic terminal of the splenic nerve to release NA and suppress macrophages to produce TNF-α (Martelli et al., 2014). Vagal efferent fibers in the gut innervate the postganglionic enteric neurons and suppress macrophage TNF-α production, via alpha-7 nicotinic receptors (Bonaz et al., 2017). The red arrow line indicates the vagus nerve pathway and regulation, whereas the blue line indicates the regulation by the sympathetic pathway. A, adrenaline; ACh, acetylcholine; ACTH, adrenocorticotrophic hormone; CRH, corticotrophin-releasing hormone; DMV, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; GI, gastrointestinal; HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal; NA, noradrenaline; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; PVN, paraventricular nucleus at the hypothalamus; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VNS, vagus nerve stimulation; α7nAChR, α-7-nicotinic ACh receptors; αAR, alpha-adrenergic receptor; βAR, beta-adrenergic receptor.