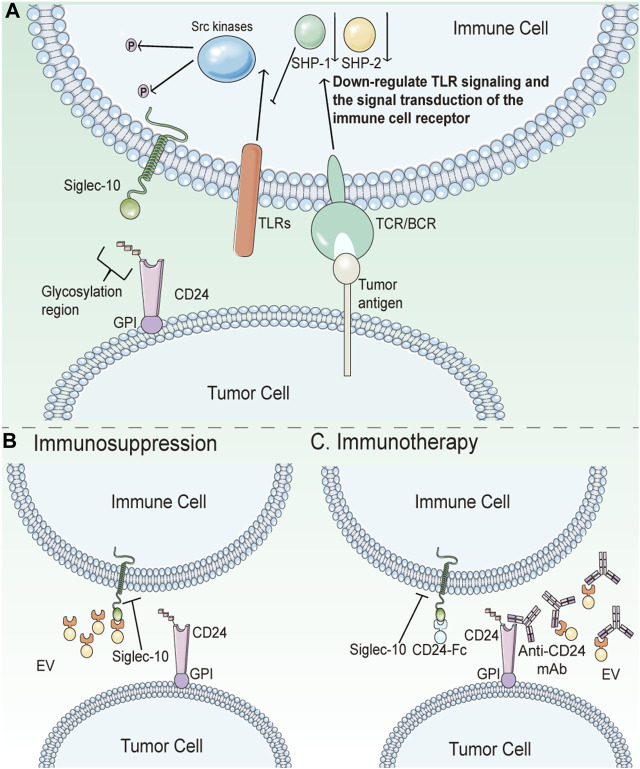
FIGURE 4.
Schematic diagram of CD24 in tumor immunotherapy. (A) CD24 helps cancer cells escape phagocytosis by interacting with Siglec10. Src family kinases are induced by ITIM or ITIM-like motifs when Siglec10’s IgV domain binds to sialic acid fragments located in the CD24 extracellular domain. After that, phosphorylated ITIM tyrosine in the cytoplasm recruits tyrosine phosphatase, thereby reducing signal transduction of the CD24-Siglec10 axis. This process will inhibit the immune activity of macrophages, reduce the phagocytosis of macrophages, and weaken the immune surveillance on tumor cells. (B) Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EV) are not phagocytic due to the expression of CD24 on them. (C) Anti-CD24 antibodies can eliminate the inhibition of CD24 on tumor cells or EV surface to macrophages and restore the clearance ability of macrophages. As an immunotherapy, CD24-Fc can trigger immunosuppression of Siglec-10 expressing immune cells, thereby protecting autoimmunity. In cancer, it is deleterious. However, CD24-Fc can block signal transduction between CD24-Sigle10 by competing as an inhibitor of CD24.