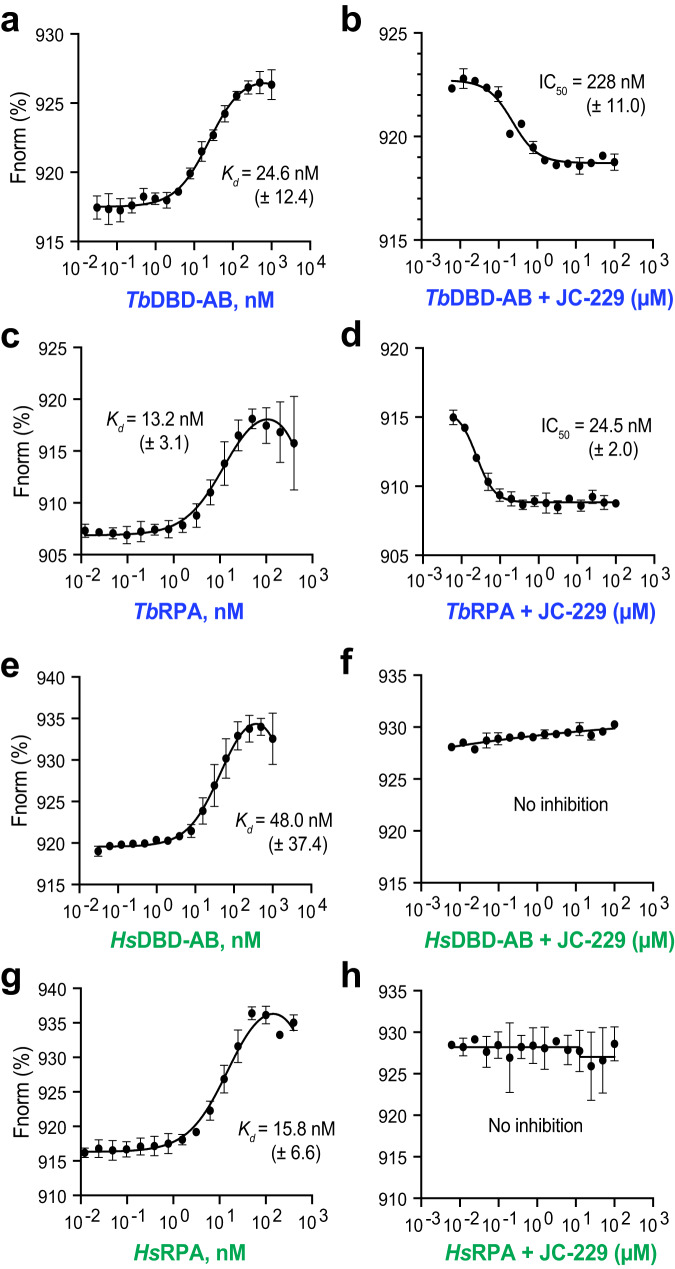
Fig. 5. MST confirms that JC-229 specifically inhibits the ssDNA-binding activity of TbRPA.
MST was performed with purified RPA proteins shown in Fig. 4i, j. The ssDNA-binding activity of recombinant RPA proteins (graphs a, c, e, g) and inhibition of the activity by JC-229 (graphs b, d, f, h) are shown. a TbRPA1 DBD-AB proteins were twofold serially diluted starting with a 1000 nM concentration and then incubated with 10 nM oligo dT32 labeled with 5´Cy5 (5´Cy5-dT32). The binding was analyzed by MST. b Serial dilutions of JC-229 were pre-incubated with 30 nM TbRPA1 DBD-AB protein and then with 10 nM 5´Cy5-dT32. Inhibition of binding was analyzed by MST. c Recombinant TbRPA complex was twofold serially diluted from 400 nM concentration and these were incubated with 10 nM 5´Cy5-dT32. The binding was analyzed by MST. d Serial dilutions of JC-229 were pre-incubated with 25 nM TbRPA complex and then with 10 nM 5´Cy5-dT32. Inhibition of binding was analyzed by MST. e, f HsRPA1 DBD-AB protein was examined as in Fig. 5a, b by MST (e: ssDNA-binding activity, f: JC-229 inhibition). g, h HsRPA complex was examined as shown in Fig. 5c, d. (g: ssDNA-binding activity, h: JC-229 inhibition). Three independent MST experiments were performed for Fig. 5a–h (n = 3). Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Statistical analysis and plotting were performed with GraphPad Prism software. Kd and IC50 values were obtained with one site binding total and standard 4-PL curve, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.