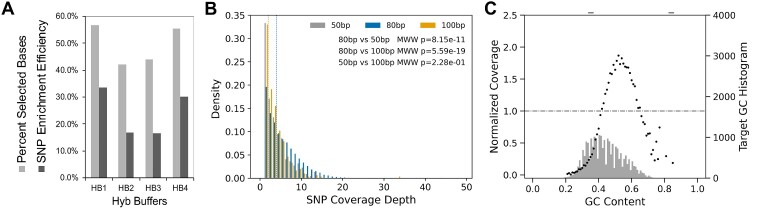
Figure 2.
Optimization of CNERs hybridization capture of SNPs in four modern horse samples. (A) Enrichment efficiency for four hybridization buffers with pH varying from 6.5 to 8.0 (HB1 - 4). Light grey bars show the Percent Selected Bases determined using Picard tools and dark grey bars show the SNP enrichment efficiency. Values presented are the average of three experiments for HB1 and HB4 buffers and exact values for a single experiment for HB2 and HB3. (B) Histogram density plots of SNP coverage depth for three CNER lengths. SNPs captured with 80bp CNERs (blue bars) result in significantly higher coverage compared to SNPs captured with 50 bp (grey bars) or 100 bp (orange bars) CNERs; p-value is from a Mann–Whitney Wilcoxon test. Dotted lines indicate the mean coverage for each CNERs length. (C) Mean of normalized coverage (primary Y-axis) plotted across GC content of CNER target regions show that regions with 43–65% GC have sample-normalized coverage of 1 or higher. A histogram of GC bins across the target regions is shown in the secondary Y-axis.