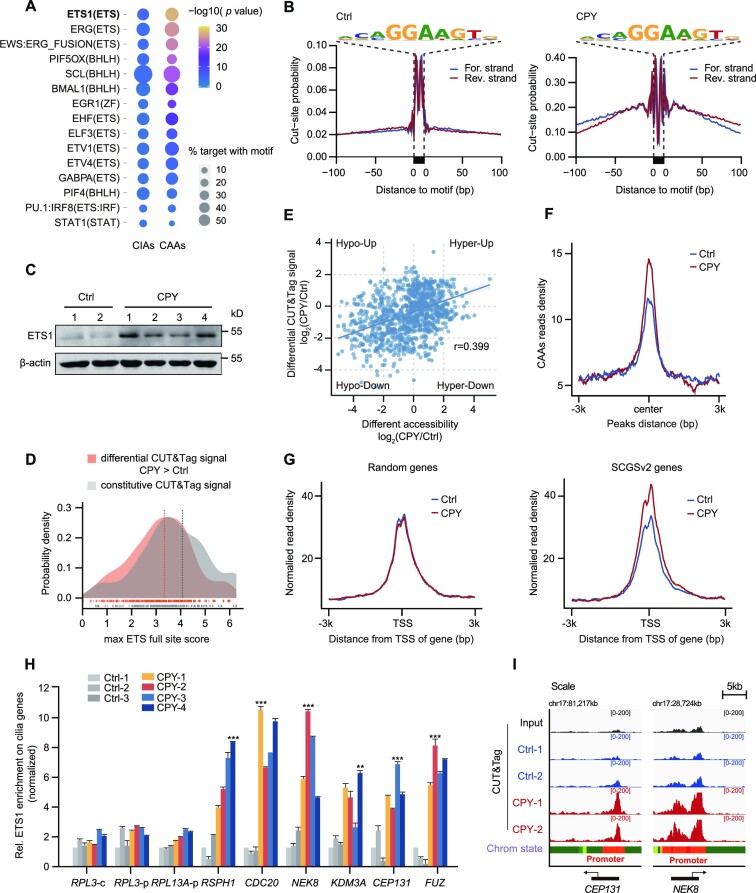
Figure 4.
ETS1 is recruited to CAAs and leads to increased expression of cilia genes. (A) Top-ranked enriched motifs among CAAs and CIAs are listed, as determined using HOMER2 algorithms. The circle size represents the percentage of motifs in the target regions, and the colour represents the P-value. (B) ATAC-seq footprint at the ETS motif site in controls and patients. Insertions per site are normalized to have the same average number of insertions 200–500 bp away from the motif. (C) Western blotting analysis of total ETS1 protein expression in Ctrl and CPY. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (D) Distribution of motif scores of sites within ETS1 CUT&Tag peaks in PBMCs, either those that gave more signal in CPY than in the Ctrl (differential) or those that were not significantly different (constitutive). The maximum scoring ETS full site within each CUT&Tag peak was used. The constitutive peaks have a higher mean motif score than the differential peaks (Mann–Whitney U-test, P < 1 × 10−32). (E) Spearman's correlation of differential ETS1 CUT&Tag signals in accessible regions and differential accessibility in CPY versus Ctrl (r = 0.399). (F) The enrichment of ETS1 CUT&Tag signals at CAAs in both Ctrl and CPY. Tracks are centred at the peaks and extend ± 3 kb. (G) Enrichment plots showing normalized read densities of ETS1 CUT&Tag signals at the TSS for randomly selected genes (n = 700, left) and SCGSv2 genes (right) in both Ctrl and CPY. Tracks are centred at the TSS, extending ± 3 kb. (H) The relative levels of cilia genes flanking CAAs in Ctrl and CPY measured using ETS1 ChIP-qPCR in PBMCs. ETS1 enrichment for RPL3-c (coding region) served as the negative control, and ETS1 enrichment for RPL3-p (promoter region) and RPL13A-p (promoter region) served as positive controls, as previously described. The enrichment of ETS1 is normalized to 10% input. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, as determined using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. (I) IGV snapshot showing the ETS1 CUT&Tag signals of PBMCs in Ctrl and CPY at chromosome 17 loci of cilia genes CEP131 and NEK8.