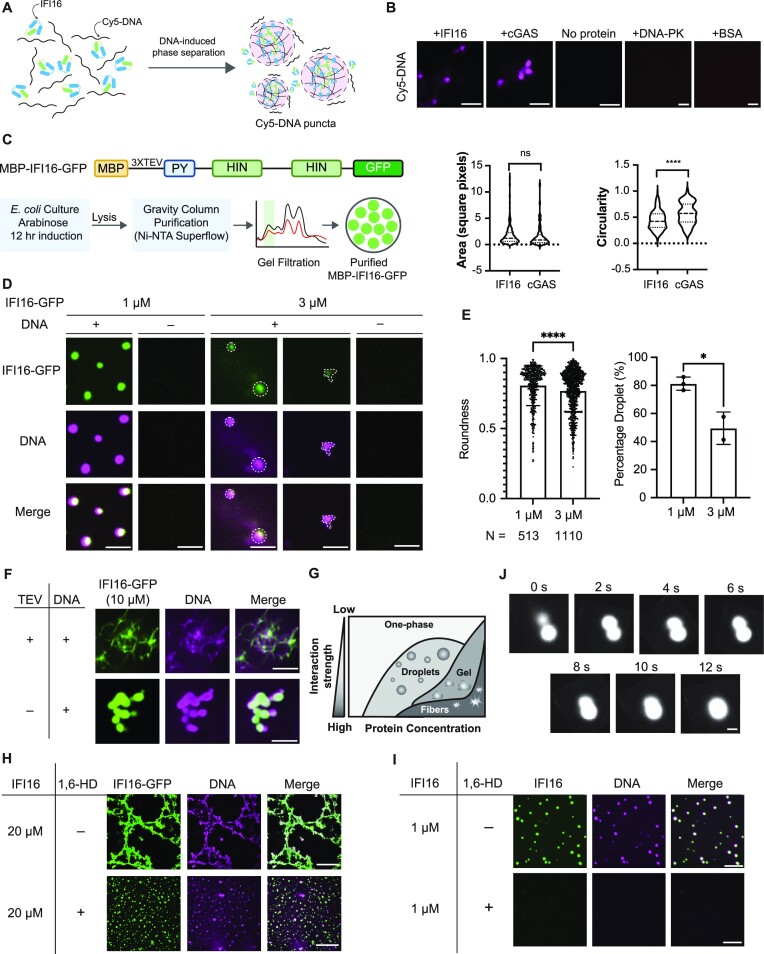
Figure 1.
IFI16 forms droplets and filaments mediated by LLPS in vitro in the presence of DNA. (A) Schematics of IFI16-DNA interactions leading to LLPS. Green and blue boxes represent the pyrin domain and HIN domains of IFI16 respectively. (B) Images of 5 μM Cy5-DNA in the presence or absence of purified 5 μM cGAS or IFI16. Areas and circularities of Cy5-DNA puncta were quantified using Fiji. Scale bar, 5 μm. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired t-test. (C) Construct of MBP-IFI16-GFP and schematics of the optimized protocol for purifying MBP-IFI16-GFP. MBP, maltose-binding protein. PY, pyrin domain. Monomeric eGFP was used. (D) Representative images of IFI16-GFP LLPS at 1 or 3 μM incubated with equimolar Cy5-DNA after TEV protease treatment. Scale bars, 1 μm. (E) Quantitative measurements of roundness and percentage of droplets of IFI16-GFP at 3 and 1 μM. Percentage droplets at each concentration was calculated as the percentage of puncta with roundness > 0.8. Roundness values were calculated using Fiji. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired t-test. Values are means ± SEMs (n = 3). (F) Representative images of 10 μM IFI16-GFP or MBP-IFI16-GFP incubated with equimolar Cy5-DNA in the presence or absence of TEV protease. Scale bar, 5 μm. (G) Schematic phase diagram representing distinct material phases that can be undertaken by LLPS proteins at varying concentrations and interaction strength amongst constituent molecules. (H) Representative images and quantification of IFI16-GFP LLPS at 20 μM in the presence or absence of 10% 1,6-HD. Scale bar, 5 μm. (I) Representative images of untagged IFI16 labeled by Alexa Fluor 488 LLPS at 1 μM in the presence or absence of 10% 1,6-HD. Scale bar, 5 μm. (J) Time-lapse micrographs of merging droplets of IFI16-GFP (20 μM) in the presence of 10% 1,6-HD and Cy5-DNA. Scale bar, 1 μm.