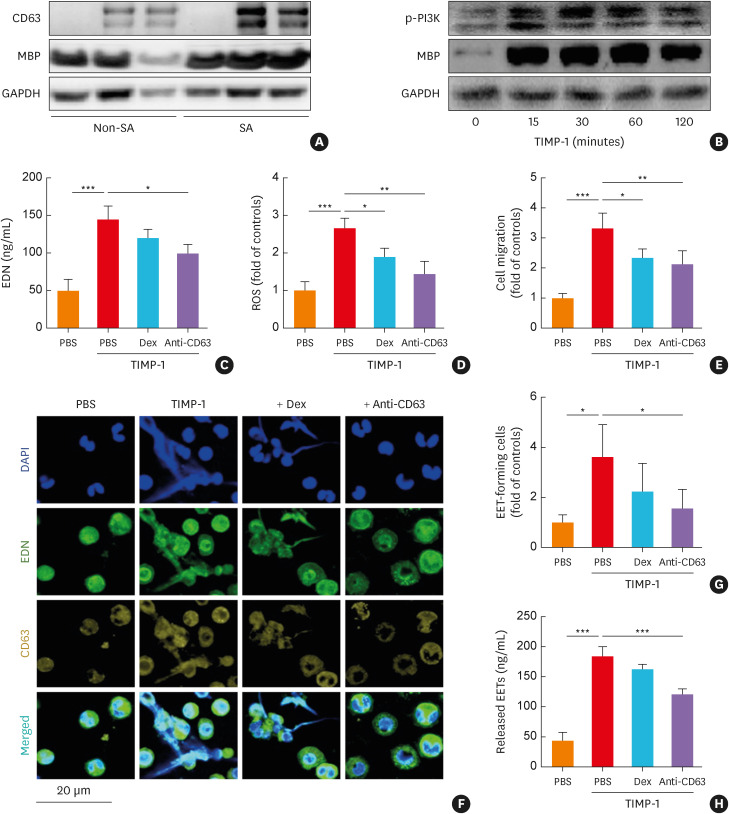
Fig. 3. The effects of TIMP-1 on human PBEs. (A) The protein expressions of CD63 and MBP in PBEs from asthmatics according to asthma severity. (B) The effect of TIMP-1 on the phosphorylation of PI3K in a time-dependent manner. TIMP-1 induced the release of (C) EDN and (D) ROS with (E) eosinophil recruitment (n = 6 for each group). (F, G) The levels of EETs were evaluated using confocal microscopy. Cells were stained with EDN (green), CD63 (yellow), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 µm. (H) The levels of released EETs were evaluated by measuring dsDNA concentrations using PicoGreen assay (n = 6 for each group). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
PBEs, peripheral blood eosinophils; DAPI, 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Dex, dexamethasone; EETs, eosinophil extracellular traps; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MBP, major basic protein; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SA, severe asthma; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1; EDN, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by one-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post hoc test.