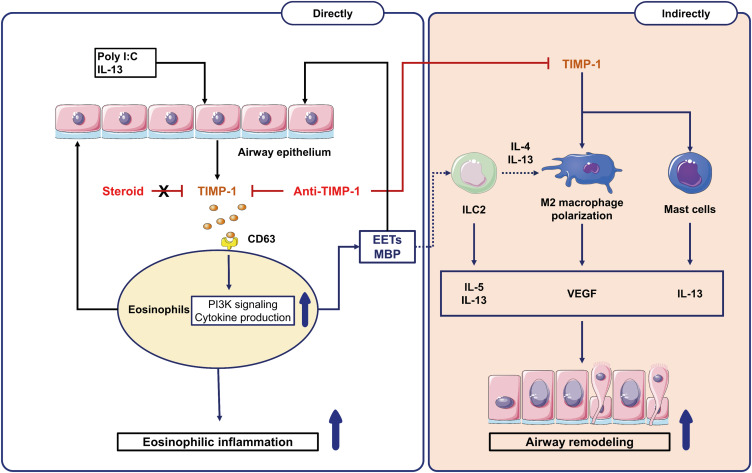
Fig. 8. Available mechanisms of TIMP-1 in type 2 SA. The exogenous (poly I:C) and endogenous factors (IL-13, eosinophils, and EETs) stimulate airway epithelial cells to release TIMP-1. The left panel showed TIMP-1-induced eosinophilic inflammation through (1) directly activating eosinophils (MBP release) and (2) indirectly activating EET formation (through CD63/PI3K signaling) in SA, which were suppressed by anti-TIMP-1 antibody (not by steroid). The right panel showed TIMP-1-induced airway remodeling via releasing proinflammatory cytokines (IL-13 and VEGF) from activated ILC2, M2 macrophages, mast cells, and eosinophils.
EETs, eosinophil extracellular traps; ILC2, group 2 innate lymphoid cells; MBP, major basic protein; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1; PI3K; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IL, interleukin; SA, severe asthma.