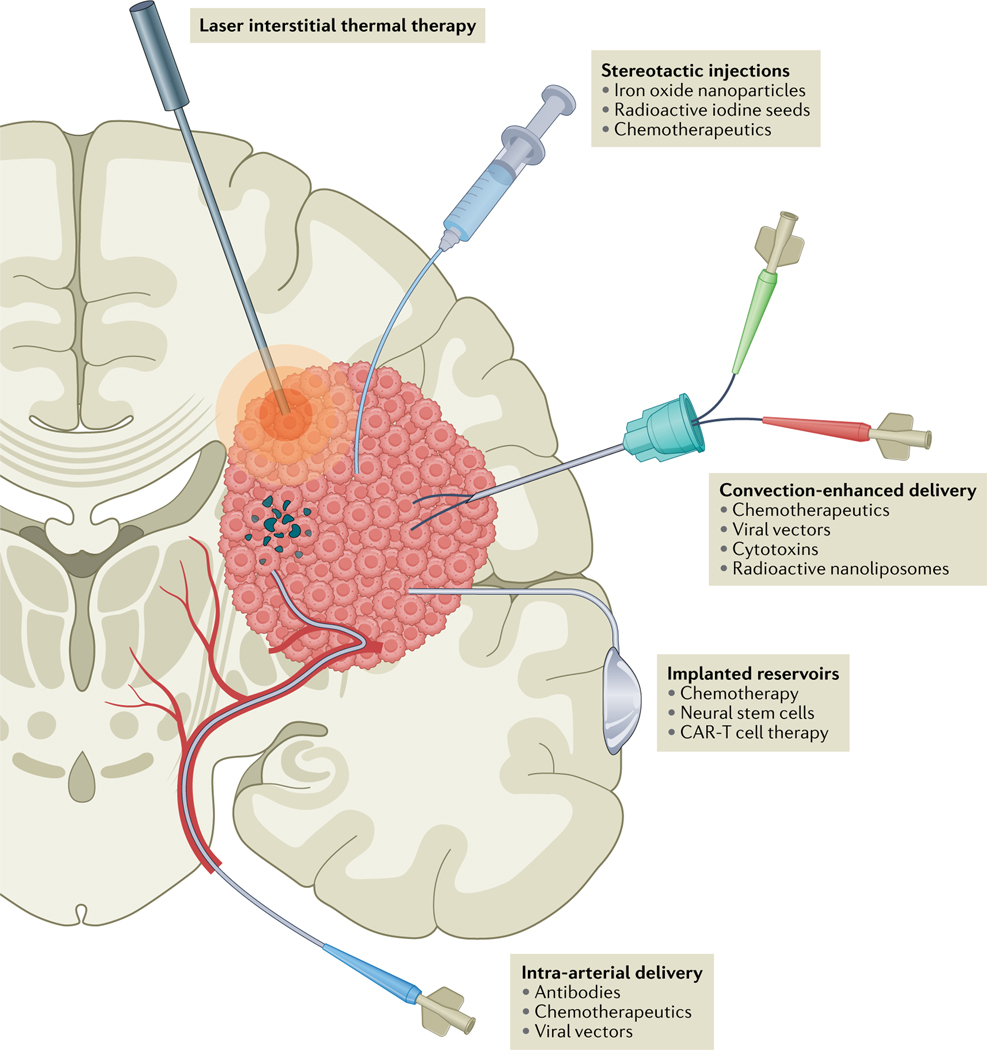
Fig. 1 |. Methods of local treatment in glioblastoma.
In laser interstitial thermal therapy, tumour tissue is heated with a laser probe, destroying the tissue and disrupting the blood–brain barrier (BBB), usually under MRI guidance. Various compounds can be injected via stereotactic injections directly into the tumour with the aid of neuronavigation, frequently coupled with intraoperative CT or MRI. Convection-enhanced delivery involves continuous injection of various compounds using a pressure gradient to improve distribution. Ommaya or Rickham reservoirs can be implanted, enabling intermittent injections of therapy over an extended period of time. Catheters can be placed in the tumour or resection cavity or in the cerebral ventricles. For intra-a rterial delivery, catheters can be positioned directly into the feeding arteries, allowing local delivery of high-dose therapeutics. This technique can be combined with BBB disruption. CAR, chimaeric antigen receptor.