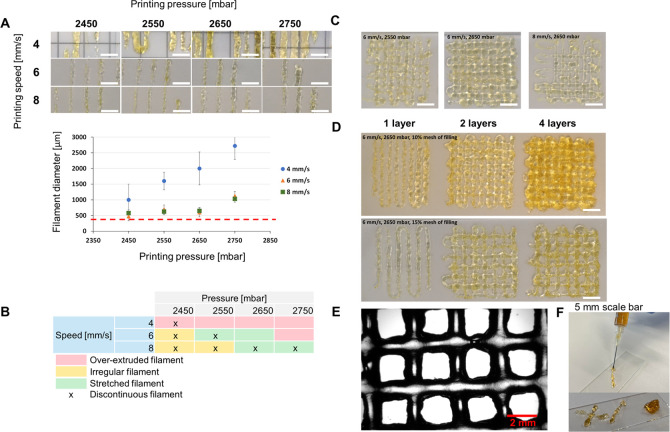
Figure 4.
Printability of biomaterial inks (HAGA20-HAMA15 at pH 7.5–8, 37 °C) and 3D printing tests. (A) Filament of printed biomaterial inks with various pressure and printing speed values. The graph illustrates how filament diameter is affected by pressure and printing speed. The red line is used as a guideline to compare the filament diameter with the actual nozzle size. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of filament diameter for each ink, presented as mean (n = 10) ± SD. (B) Printability window: an over-extruded filament (red color), irregular filament (yellow color), stretched filament (green color), or discontinuous filament (x symbol). (C) Images of two-layer printed grids to screen the optimal printing parameters. (D) Images of multilayer printing of one, two, and four layers using the optimal printing parameters and different filling percentages to determine the achievable printing resolution. (E) Example of a microscopic image of an optimal printed grid structure for Pr value calculation and stackability of 2 filament layers (6 mm/s, 2650 mbar). (F) Example of the prescreening results of injectability and stackability of biomaterial inks.