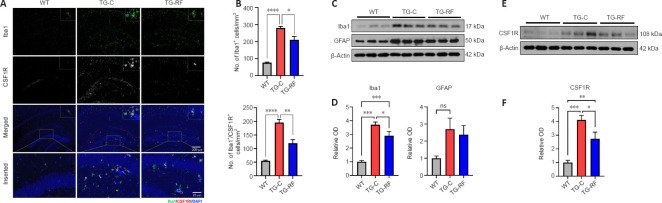
Figure 5.
Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields on Iba1 and CSF1R in the hippocampi of 5×FAD mice.
(A) Representative images of microglia (Iba1 in green) and CSF1R (red) in the hippocampi of 5×FAD mice after radiofrequency electromagnetic fields exposure. The yellow square shows the merged images at higher magnification (Inserted panel). (B) The quantification of the Iba1- and Iba1/CSF1R-positive cells in the mice hippocampus. (C and D) Representative images for Western blots and the expression levels of Iba1 and GFAP in the hippocampi of mice in the WT, TG, and TG-RF groups. (E and F) Representative images for Western blots and the expression levels of CSF1R in the hippocampi of mice in the WT, TG, and TG-RF groups. The values are shown as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 (n = 4 for B, n = 6 for D and F). CSF1R: Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; Iba1: ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1; ns: not significant; TG-C: sham-exposed TG; TG-RF: radiofrequency electromagnetic fields-exposed TG; WT: wild-type.