Figure 4.
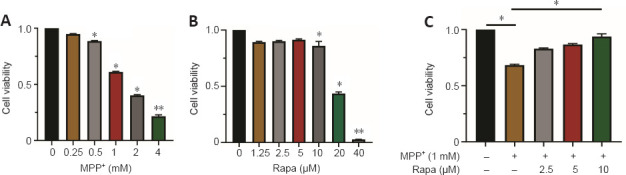
Rapa inhibits MPP+-induced decrease in PC12 cell viability.
(A) Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was used to evaluate the changes of PC12 cell viability 24 hours after MPP+ (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, or 4 mM) treatment. (B) CCK-8 assay was used to evaluate the changes of PC12 cell viability 24 hours after Rapa (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, or 40 μM) treatment. (C) After pretreatment of PC12 cells with 0, 2.5, 5, or 10 μM Rapa for 1 hour and a further 24-hour treatment with 1 mM MPP+, a CCK-8 assay was used to detect the change of cell viability. The data presented are from three different passages of cells used to seed separate 96-well plates. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 9–12 per group).*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. MPP+ (−) and Rapa (−); #P < 0.05, vs. Rapa (−) (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test;). The experiments were performed in triplicate. MPP+: 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium; Rapa: rapamycin; RSL3: methyl (1S,3R)-2-(2-chloroacetyl)-1-(4-methoxycarbonylphenyl)-1,3,4,9-tetrahyyridoindole-3-carboxylate.
