Figure 1.
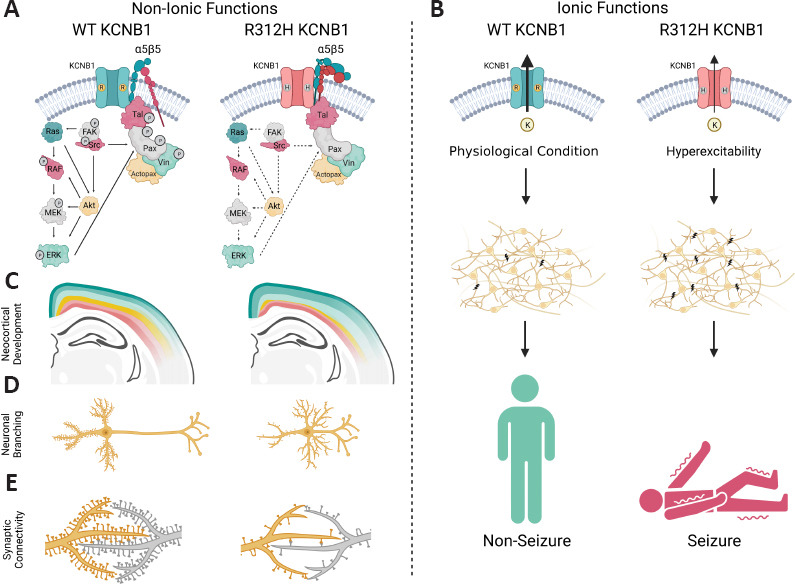
IKCs cause encephalopathy through ionic and non-ionic mechanisms.
(A) IKCs formed with integrin α5β5 dimers and KCNB1 WT (IKCKCNB1) channels recruit FAK via α5β5 integrins. FAK autophosphorylates Tyr397 (P) and then binds Src kinases. The newly formed FAK-Src dimers phosphorylate Paxillin that links the IKCKCNB1 to Ras-MAPK signaling pathways and to the actin cytoskeleton. Ras GTPases and FAK-Src dimers also cross-talk with PI3K/Akt signaling which phosphorylates several MAPK components. In turn, activated ERK phosphorylates Paxillin. In contrast, IKCs formed with R312H mutant channels (IKCR312H) fail to induce phosphorylation of the various signaling components including Vinculin, Talin-1, and Paxillin which however, still assemble with the complexes by binding to the cytoplasmic tail of integrin β5. (B) IKCs formed with either heteromeric WT/R312H or homomeric R312H channels conduct significantly smaller K+ currents compared to IKCs formed with WT channels alone. The LOF attributes of the mutant IKCs cause cortical hyperexcitability and seizures. (C) Along with impaired IKCR312H signaling, Kcnb1R312H mice, primarily the homozygotes, are affected by severe cortical neuroabnormalities, with many glutamatergic neurons destined to the Upper Layers misplaced in the Deep Layers (yellow). (D) The neurons of Kcnb1R312H mice develop shorter dendrites compared to WT neurons, and abnormal arborizations around the soma. (E) Synaptic functionality is significantly reduced in the brains of Kcnb1R312H homozygotes. This goes on par with the increased numbers of immature spines in the pyramidal neurons of those animals. α5β5: Integrin alpha5-beta5; Actopax: actopaxin; Akt: protein kinase B; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK: focal adhesion kinase; KCNB1: voltage-gated potassium channel subfamily 2, member 1; MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; P: phosphate; Pax: paxillin; RAF: rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma kinase; Ras: rat sarcoma virus GTPase; Src: Src family kinase; Tal: talin-1; Vin: vinculin. Created with BioRender.com.
