Figure 1.
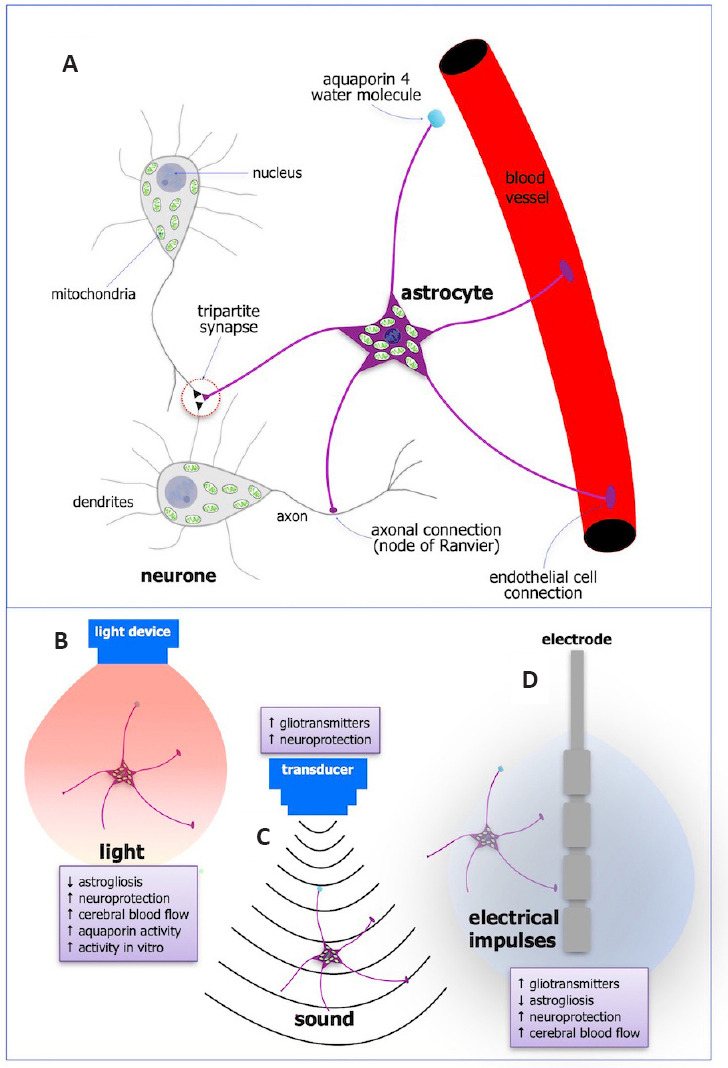
Schematic diagrams of the anatomy and functions of astrocytes (A) and the major effects on their function after photobiomodulation (B), ultrasound (C), and deep brain stimulation (D).
Astrocytes have a cell body with a nucleus and many mitochondria, and processes that extend to every neuronal synapse (tripartite synapse), to axons at the nodes of Ranvier, and to endothelial cells lining blood vessels. They also have aquaporin 4 water molecules on their end-feet (A). Taken all together, astrocytes are in a strategic position to influence many aspects of brain function. Their activity is influenced greatly after external treatment of light (photobiomodulation; B), sound (ultrasound; C), and electricity (deep brain stimulation; D), and these are listed in the small purple boxes next to each treatment. Created with Apple Keynote.
