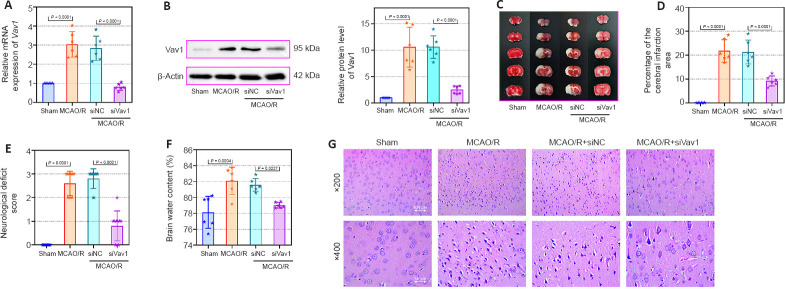
Figure 2.
Vav1 knockdown decreases brain infarction area and neuronal injury in MCAO/R rats.
(A) Vav1 mRNA expression (normalized to the sham group) in MCAO/R rats, as detected by qPCR. (B) Vav1 protein expression (normalized to the sham group) in MCAO/R rats, as detected by western blot. (C) TTC staining images of cerebral infarction area in MCAO/R rat brain tissues. MCAO/R rats showed increased infarction area compared with sham rats, while Vav1 knockdown reversed this effect. The white area represents the infarction area. (D) Quantitation of the cerebral infarction results. (E) Neurological deficiency scores of MCAO/R rats. (F) Brain water content of MCAO/R rats. (G) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the cerebral infarction area in MCAO/R rats. The MCAO/R rats showed more damage in the ischemic penumbra than sham rats, but inhibition of Vav1 expression reversed this effect. Scale bars: 100 μm (upper) and 50 μm (lower). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 10 (E), n = 6 (others)), and were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The experiments were repeated three times. MCAO/R: Middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TTC staining: triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining; Vav1: Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1.